The life-cycle of Toxoplasma gondii reviewed using animations
- PMID: 33228743
- PMCID: PMC7686686
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-020-04445-z
The life-cycle of Toxoplasma gondii reviewed using animations
Abstract
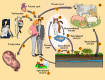
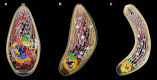
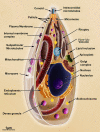
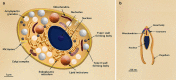
Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite that is the causative agent of toxoplasmosis, an infection with high prevalence worldwide. Most of the infected individuals are either asymptomatic or have mild symptoms, but T. gondii can cause severe neurologic damage and even death of the fetus when acquired during pregnancy. It is also a serious condition in immunodeficient patients. The life-cycle of T. gondii is complex, with more than one infective form and several transmission pathways. In two animated videos, we describe the main aspects of this cycle, raising questions about poorly or unknown issues of T. gondii biology. Original plates, based on electron microscope observations, are also available for teachers, students and researchers. The main goal of this review is to provide a source of learning on the fundamental aspects of T. gondii biology to students and teachers contributing for better knowledge and control on this important parasite, and unique cell model. In addition, drawings and videos point to still unclear aspects of T. gondii lytic cycle that may stimulate further studies.
Keywords: Apicomplexa; Cell biology; Life-cycle; Parasite; Parasitology; Protozoology; Toxoplasmosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- CDC. Toxoplasmosis - epidemiology & risk factors. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2018. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/toxoplasmosis/epi.html. Accessed 06 Aug 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

