Plasma Concentrations and Safety of Lopinavir/Ritonavir in COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 33230045
- PMCID: PMC7808275
- DOI: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000838
Plasma Concentrations and Safety of Lopinavir/Ritonavir in COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
Background: Although the efficacy of lopinavir/ritonavir has not been proven, it has been proposed as an off-label treatment for COVID-19. Previously, it has been reported that the plasma concentrations of lopinavir significantly increase in inflammatory settings. As COVID-19 may be associated with major inflammation, assessing the plasma concentrations and safety of lopinavir in COVID-19 patients is essential.
Methods: Real-world COVID-19 data based on a retrospective study.
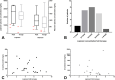
Results: Among the 31 COVID-19 patients treated with lopinavir/ritonavir between March 18, 2020 and April 1, 2020, higher lopinavir plasma concentrations were observed, which increased by 4.6-fold (interquartile range: 3.6-6.2), compared with the average plasma concentrations in HIV. Lopinavir concentrations in all except one patient were above the upper limit of the concentration range of HIV treatment. Approximately one to 5 patients prematurely stopped treatment mainly because of an ADR related to hepatic or gastrointestinal disorders.
Conclusions: Lopinavir plasma concentrations in patients with moderate-to-severe COVID-19 were higher than expected, and they were associated with the occurrence of hepatic or gastrointestinal adverse drug reactions. However, a high plasma concentration may be required for in vivo antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2, as suggested by previous studies. Therefore, in the absence of adverse drug reaction, lopinavir dosage should not be reduced. Caution is essential because off-label use can be associated with a new drug safety profile.
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kanters S, Socias ME, Paton NI, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of second-line antiretroviral therapy for treatment of HIV/AIDS: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet HIV. 2017;4:e433–e441. - PubMed
-
- Kim UJ, Won EJ, Kee SJ, et al. Combination therapy with lopinavir/ritonavir, ribavirin and interferon-α for middle east respiratory syndrome. Antivir Ther. 2016;21:455–459. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

