Influence of patient characteristics on chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 33230103
- PMCID: PMC7683530
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19774-x
Influence of patient characteristics on chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
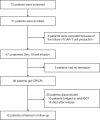
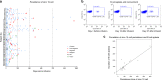
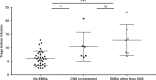
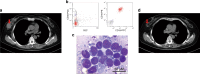
CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CD19 CAR T) therapy has shown high remission rates in patients with refractory/relapsed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (r/r B-ALL). However, the long-term outcome and the factors that influence the efficacy need further exploration. Here we report the outcome of 51 r/r B-ALL patients from a non-randomized, Phase II clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.gov number: NCT02735291). The primary outcome shows that the overall remission rate (complete remission with or without incomplete hematologic recovery) is 80.9%. The secondary outcome reveals that the overall survival (OS) and relapse-free survival (RFS) rates at 1 year are 53.0 and 45.0%, respectively. The incidence of grade 4 adverse reactions is 6.4%. The trial meets pre-specified endpoints. Further analysis shows that patients with extramedullary diseases (EMDs) other than central nervous system (CNS) involvement have the lowest remission rate (28.6%). The OS and RFS in patients with any subtype of EMDs, higher Tregs, or high-risk genetic factors are all significantly lower than that in their corresponding control cohorts. EMDs and higher Tregs are independent high-risk factors respectively for poor OS and RFS. Thus, these patient characteristics may hinder the efficacy of CAR T therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work. There is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service, and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the paper entitled. We declare that no competing interests exist regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

