Ionizing radiation results in a mixture of cellular outcomes including mitotic catastrophe, senescence, methuosis, and iron-dependent cell death
- PMID: 33230108
- PMCID: PMC7684309
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-03209-y
Ionizing radiation results in a mixture of cellular outcomes including mitotic catastrophe, senescence, methuosis, and iron-dependent cell death
Abstract
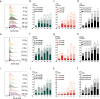
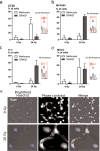
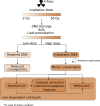
Radiotherapy is commonly used as a cytotoxic treatment of a wide variety of tumors. Interestingly, few case reports underlined its potential to induce immune-mediated abscopal effects, resulting in regression of metastases, distant from the irradiated site. These observations are rare, and apparently depend on the dose used, suggesting that dose-related cellular responses may be involved in the distant immunogenic responses. Ionizing radiation (IR) has been reported to elicit immunogenic apoptosis, necroptosis, mitotic catastrophe, and senescence. In order to link a cellular outcome with a particular dose of irradiation, we performed a systematic study in a panel of cell lines on the cellular responses at different doses of X-rays. Remarkably, we observed that all cell lines tested responded in a similar fashion to IR with characteristics of mitotic catastrophe, senescence, lipid peroxidation, and caspase activity. Iron chelators (but not Ferrostatin-1 or vitamin E) could prevent the formation of lipid peroxides and cell death induced by IR, suggesting a crucial role of iron-dependent cell death during high-dose irradiation. We also show that in K-Ras-mutated cells, IR can induce morphological features reminiscent of methuosis, a cell death modality that has been recently described following H-Ras or K-Ras mutation overexpression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
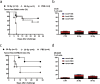
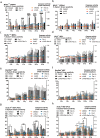
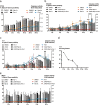
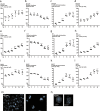

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

