An enolase inhibitor for the targeted treatment of ENO1-deleted cancers
- PMID: 33230295
- PMCID: PMC7744354
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-020-00313-3
An enolase inhibitor for the targeted treatment of ENO1-deleted cancers
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: An enolase inhibitor for the targeted treatment of ENO1-deleted cancers.Nat Metab. 2021 Jan;3(1):122. doi: 10.1038/s42255-020-00335-x. Nat Metab. 2021. PMID: 33340032 No abstract available.
Abstract
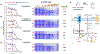
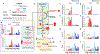
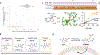
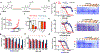
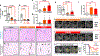
Inhibiting glycolysis remains an aspirational approach for the treatment of cancer. We have previously identified a subset of cancers harbouring homozygous deletion of the glycolytic enzyme enolase (ENO1) that have exceptional sensitivity to inhibition of its redundant paralogue, ENO2, through a therapeutic strategy known as collateral lethality. Here, we show that a small-molecule enolase inhibitor, POMHEX, can selectively kill ENO1-deleted glioma cells at low-nanomolar concentrations and eradicate intracranial orthotopic ENO1-deleted tumours in mice at doses well-tolerated in non-human primates. Our data provide an in vivo proof of principle of the power of collateral lethality in precision oncology and demonstrate the utility of POMHEX for glycolysis inhibition with potential use across a range of therapeutic settings.
Figures

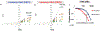



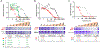



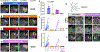


References
-
- Fonvielle M, Mariano S. & Therisod M. New inhibitors of rabbit muscle triose-phosphate isomerase. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 15, 2906–2909 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Anderson VE, Weiss PM & Cleland WW Reaction Intermediate Analogues for Enolase. Biochemistry 23, 2779–2786 (1984). - PubMed
-
- P B-H et al. Decreased red cell enolase activity in a 40-year-old woman with compensated haemolysis. Scand. J. Haematol. 33, 401–404 (1984). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RP140612/Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas)/International
- R01 CA225955/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RSG-15-145-01-CDD/American Chemical Society (ACS)/International
- P50 CA127001/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

