A portable scanner for magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
- PMID: 33230306
- PMCID: PMC8597947
- DOI: 10.1038/s41551-020-00641-5
A portable scanner for magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
Abstract
Access to scanners for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is typically limited by cost and by infrastructure requirements. Here, we report the design and testing of a portable prototype scanner for brain MRI that uses a compact and lightweight permanent rare-earth magnet with a built-in readout field gradient. The 122-kg low-field (80 mT) magnet has a Halbach cylinder design that results in a minimal stray field and requires neither cryogenics nor external power. The built-in magnetic field gradient reduces the reliance on high-power gradient drivers, lowering the overall requirements for power and cooling, and reducing acoustic noise. Imperfections in the encoding fields are mitigated with a generalized iterative image reconstruction technique that leverages previous characterization of the field patterns. In healthy adult volunteers, the scanner can generate T1-weighted, T2-weighted and proton density-weighted brain images with a spatial resolution of 2.2 × 1.3 × 6.8 mm3. Future versions of the scanner could improve the accessibility of brain MRI at the point of care, particularly for critically ill patients.
Figures
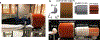
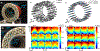

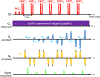

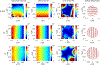
Comment in
-
Compact brain MRI.Nat Biomed Eng. 2021 Mar;5(3):201-202. doi: 10.1038/s41551-021-00702-3. Nat Biomed Eng. 2021. PMID: 33727710 No abstract available.
-
Device downsizing via signal enhancement.Nat Biomed Eng. 2021 Mar;5(3):195-196. doi: 10.1038/s41551-021-00708-x. Nat Biomed Eng. 2021. PMID: 33727712 No abstract available.
References
-
- Beckmann U, Gillies DM, Berenholtz SM, Wu AW & Pronovost P. Incidents relating to the intra-hospital transfer of critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 30, 1579–1585 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Mathur AM, Neil JJ, McKinstry RC & Inder TE Transport, monitoring, and successful brain MR imaging in unsedated neonates. Pediatr. Radiol. 38, 260–264 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Warf BC & East African Neurosurgical Research Collaboration. Pediatric hydrocephalus in East Africa: prevalence, causes, treatments, and strategies for the future. World Neurosurg. 73, 296–300 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

