The cGMP system in normal and degenerating mouse neuroretina: New proteins with cGMP interaction potential identified by a proteomics approach
- PMID: 33230839
- PMCID: PMC8359485
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.15251
The cGMP system in normal and degenerating mouse neuroretina: New proteins with cGMP interaction potential identified by a proteomics approach
Abstract
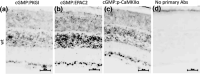
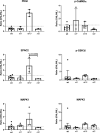
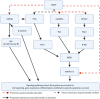
The hereditary disease Retinitis pigmentosa results in severe vision loss due to photoreceptor degeneration by unclear mechanisms. In several disease models, the second messenger cGMP accumulates in the degenerating photoreceptors, where it may over-activate specific cGMP-interacting proteins, like cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Moreover, interventions that counteract the activity of these proteins lead to reduced photoreceptor cell death. Yet there is little or no information whether other than such regular cGMP-interactors are present in the retina, which we, therefore, investigated in wild-type and retinal degeneration (rd1, rd10, and rd2) mouse models. An affinity chromatography based proteomics approach that utilized immobilized cGMP analogs was applied to enrich and select for regular and potentially new cGMP-interacting proteins as identified by mass spectrometry. This approach revealed 12 regular and 10 potentially new retinal cGMP-interacting proteins (e.g., EPAC2 and CaMKIIα). Several of the latter were found to be expressed in the photoreceptors and to have proximity to cGMP and may thus be of interest when defining prospective therapeutic targets or biomarkers for retinal degeneration.
Keywords: Chemical proteomics; Photoreceptors; Retinal degeneration; cGMP; cGMP-interacting proteins.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Neurochemistry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International Society for Neurochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
FS is employed at Biolog Life Science Institute, which offers certain analogs and other products of this study on a commercial basis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced cGMP Interactor Rap Guanine Exchange Factor 4 (EPAC2) Expression and Activity in Degenerating Photoreceptors: A Neuroprotective Response?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 21;23(9):4619. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094619. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563009 Free PMC article.
-
Different effects of valproic acid on photoreceptor loss in Rd1 and Rd10 retinal degeneration mice.Mol Vis. 2014 Nov 4;20:1527-44. eCollection 2014. Mol Vis. 2014. PMID: 25489226 Free PMC article.
-
The photoreceptor protective cGMP-analog Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS interacts with cGMP-interactors PKGI, PDE1, PDE6, and PKAI in the degenerating mouse retina.J Comp Neurol. 2023 Jun;531(8):935-951. doi: 10.1002/cne.25475. Epub 2023 Mar 29. J Comp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36989379
-
The cGMP Pathway and Inherited Photoreceptor Degeneration: Targets, Compounds, and Biomarkers.Genes (Basel). 2019 Jun 14;10(6):453. doi: 10.3390/genes10060453. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31207907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Do cGMP Levels Drive the Speed of Photoreceptor Degeneration?Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1074:327-333. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-75402-4_40. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29721960 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced cGMP Interactor Rap Guanine Exchange Factor 4 (EPAC2) Expression and Activity in Degenerating Photoreceptors: A Neuroprotective Response?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 21;23(9):4619. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094619. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563009 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics identifies multiple retinitis pigmentosa associated proteins involved in retinal degeneration in a mouse model bearing a Pde6b mutation.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 27;14(1):22090. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72821-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39333705 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Kinase Activity Profiling and Phosphoproteomics of rd10 Mouse Retina during cGMP-Dependent Retinal Degeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 19;25(6):3446. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063446. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542418 Free PMC article.
-
The Sleep Quality- and Myopia-Linked PDE11A-Y727C Variant Impacts Neural Physiology by Reducing Catalytic Activity and Altering Subcellular Compartmentalization of the Enzyme.Cells. 2023 Dec 14;12(24):2839. doi: 10.3390/cells12242839. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38132157 Free PMC article.
-
The sleep quality- and myopia-linked PDE11A-Y727C variant impacts neural physiology by reducing catalytic activity and altering subcellular compartmentalization of the enzyme.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 17:2023.11.16.567422. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.16.567422. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cells. 2023 Dec 14;12(24):2839. doi: 10.3390/cells12242839. PMID: 38014312 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Arango‐Gonzalez, B., Trifunović, D., Sahaboglu, A., Kranz, K., Michalakis, S., Farinelli, P., Koch, S., Koch, F., Cottet, S., Janssen‐Bienhold, U., Dedek, K., Biel, M., Zrenner, E., Euler, T., Ekström, P., Ueffing, M., & Paquet‐Durand, F. (2014). Identification of a common non‐apoptotic cell death mechanism in hereditary retinal degeneration. PLoS One, 9, 1–11. 10.1371/journal.pone.0112142 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aulia, J. A., Sakagami, H., Kikkawa, S., & Terashima, T. (2015). Expression of beta subunit 2 of Ca 2+ /calmodulin‐dependent protein kinase I in the developing rat retina. Kobe Journal of Medical Sciences, 61, 115–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

