Reduction of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infectivity by admissible concentration of ozone gas and water
- PMID: 33230863
- PMCID: PMC7753712
- DOI: 10.1111/1348-0421.12861
Reduction of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infectivity by admissible concentration of ozone gas and water
Abstract
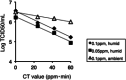
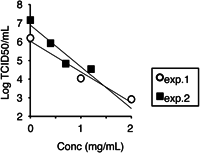
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is causing the global coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Because complete elimination of SARS-CoV-2 appears difficult, decreasing the risk of transmission is important. Treatment with 0.1 and 0.05 ppm ozone gas for 10 and 20 hr, respectively, decreased SARS-CoV-2 infectivity by about 95%. The magnitude of the effect was dependent on humidity. Treatment with 1 and 2 mg/L ozone water for 10 s reduced SARS-CoV-2 infectivity by about 2 and 3 logs, respectively. Our results suggest that low-dose ozone, in the form of gas and water, is effective against SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; TCID50; humidity; ozone gas; ozone water.
© 2020 The Societies and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
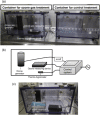
References
-
- World Health Organization . COVID‐19 situation reports. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

