Analysis of the mylohyoid nerve in elderly Japanese cadavers for dental implant surgery
- PMID: 33230980
- PMCID: PMC7853905
- DOI: 10.1002/cre2.341
Analysis of the mylohyoid nerve in elderly Japanese cadavers for dental implant surgery
Abstract
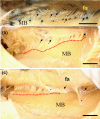
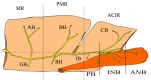
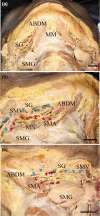
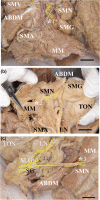
Objectives: Injury to the mandibular nerve (MN) branches may cause pain and irregular occlusal movement during mastication after mandibular dental treatments. Growing evidence indicates that the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) plays a key role in the development of peripheral sensitization and the associated enhanced pain, suggesting it may be a sign to ensure a safe and reliable dental implant treatment. Our focus was on the distribution of the MN branches and their communication with the lingual nerve (LN), the localized expression of CGRP, and the identification of a pain area related to the mylohyoid muscle (MM) fascia in the mandibular floor.
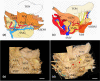
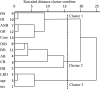
Material and methods: In this study, MM samples from 440 sides of 303 human cadavers aged 61-103 years were examined microscopically and immunohistochemically. These data were further evaluated by the use of principal component analysis.
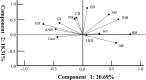
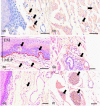
Results: A complex but weak attachment site was identified for the fascia of the MM. CGRP expression was mainly located in small vessels and was scattered throughout the whole fascia of the MM. Communication between the MN and LN was found in 62.5% (275/440) of the samples. The results from the principal component analysis showed that the positive contributions were from the descending branch in the premolar region (correlation coefficient value R = 0.665), the ascending branch in the molar region (R = 0.709) and the intermediate branch of the digastric branch (R = 0.720) in component 1. In the fascia off the MM, strongly labeled CGRP-positive cells were also found around the blood vessels and the nerve.
Conclusions: The findings reported in this study indicate that there is a risk of damage when pulling the fascia off the MM at the border of the molar and premolar regions during dental implant surgery.
Keywords: communication; mandible; mylohyoid muscle; mylohyoid nerve; pain.
© 2020 The Authors. Clinical and Experimental Dental Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An unusual communication between the mylohyoid and lingual nerves in man: its significance in lingual nerve injury.Indian J Dent Res. 2010 Jan-Mar;21(1):141-2. doi: 10.4103/0970-9290.62792. Indian J Dent Res. 2010. PMID: 20427927
-
Supernumerary muscle bundles in the submental triangle: their positional relationships according to innervation.Surg Radiol Anat. 2004 Jun;26(3):245-53. doi: 10.1007/s00276-004-0227-1. Epub 2004 Feb 11. Surg Radiol Anat. 2004. PMID: 14872289
-
Variant innervation of the mylohyoid muscle by the lingual nerve.Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2022;81(4):1079-1081. doi: 10.5603/FM.a2021.0118. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2022. PMID: 34750801 Review.
-
Ultrasonographic characterization of lingual structures pertinent to oral, periodontal, and implant surgery.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2020 Apr;31(4):352-359. doi: 10.1111/clr.13573. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2020. PMID: 31925829 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory innervation of mandibular teeth by the nerve to the mylohyoid: implications in local anesthesia.Clin Anat. 2007 Aug;20(6):591-5. doi: 10.1002/ca.20479. Clin Anat. 2007. PMID: 17352413 Review.
Cited by
-
Localizing the nerve to the mylohyoid using the mylohyoid triangle.Anat Cell Biol. 2021 Sep 30;54(3):304-307. doi: 10.5115/acb.21.019. Anat Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33941711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambalavanar, R. , Dessem, D. , Moutanni, A. , Yallampalli, C. , Yallampalli, U. , Gangula, P. , & Bai, G. (2006). Muscle injury in rats induces upregulation of inflammatory cytokines in injured muscle and calcitonin gene‐related peptide in dorsal root ganglia innervating the injured muscle. Neuroscience, 143, 875–884. - PubMed
-
- Aoki, C. , Nara, T. , & Kageyama, I. (2011). Relative position of the mylohyoid line on dentulous and edentulous mandibles. Okajimas Folia Anatomica Japonica, 87, 71–76. - PubMed
-
- Azuma, Y. , Miwa, Y. , & Sato, I. (2016). Expression of CGRP in embryonic mouse masseter muscle. Annals of Anatomy, 206, 34–47. - PubMed
-
- Bell, D. , & McDermott, B. J. (1996). Calcitonin gene‐related peptide in the cardiovascular system: Characterization of receptor populations and their (patho)physiological significance. Pharmacological Reviews, 48, 253–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

