Handheld reflectance confocal microscopy: Personalized and accurate presurgical delineation of lentigo maligna (melanoma)
- PMID: 33231342
- PMCID: PMC7984324
- DOI: 10.1002/hed.26545
Handheld reflectance confocal microscopy: Personalized and accurate presurgical delineation of lentigo maligna (melanoma)
Abstract
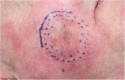
Background: The surgical treatment of lentigo maligna melanoma is associated with high rates of local recurrence. Handheld reflectance confocal microscopy (HH-RCM) allows for in vivo presurgical detection of subclinical lentigo maligna (melanoma) (LM/LMM).
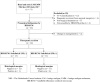
Methods: A single-center retrospective study from December 2015 to July 2017. Frequency and extent of negative surgical margins, and the diagnostic accuracy of presurgical mapping by HH-RCM was determined.
Results: Twenty-six consecutive patients with LM/LMM were included. In 45.8%, HH-RCM detected subclinical LM with a sensitivity of 0.90 and specificity of 0.86. The management was changed in two (7.7%) patients. Of the 24 remaining lesions, 95.8% were excised with negative margins with a mean histological margin of 3.1 and 5.3 mm for LM and LMM, respectively. At a mean follow-up of 36.7 months, there was one (4.8%) confirmed recurrence.
Conclusions: Our method of presurgical delineation by HH-RCM appears to provide a reliable method for the surgical treatment of LM/LMM with a limited rate of overtreatment.
Keywords: diagnostic accuracy; lentigo maligna; presurgical mapping; reflectance confocal microscopy.
© 2020 The Authors. Head & Neck published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures


References
-
- Cohen LM. Management of lentigo maligna and lentigo maligna melanoma with tangential paraffin‐embedded sections. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31(4):691‐692. - PubMed
-
- Greveling K, Wakkee M, Nijsten T, van den Bos RR, Hollestein LM. Epidemiology of lentigo maligna and lentigo maligna melanoma in the Netherlands, 1989‐2013. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136(10):1955‐1960. - PubMed
-
- Swetter SM, Boldrick JC, Jung SY, Egbert BM, Harvell JD. Increasing incidence of lentigo maligna melanoma subtypes: northern California and national trends 1990‐2000. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125(4):685‐691. - PubMed
-
- McKenna JK, Florell SR, Goldman GD, Bowen GM. Lentigo maligna/lentigo maligna melanoma: current state of diagnosis and treatment. Dermatologic. 2006;32(4):493‐504. - PubMed
-
- Bosbous MW, Dzwierzynski WW, Neuburg M. Staged excision of lentigo maligna and lentigo maligna melanoma: a 10‐year experience. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124(6):1947‐1955. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

