Blood serum amyloid A as potential biomarker of pembrolizumab efficacy for patients affected by advanced non-small cell lung cancer overexpressing PD-L1: results of the exploratory "FoRECATT" study
- PMID: 33231726
- PMCID: PMC8139913
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-020-02788-1
Blood serum amyloid A as potential biomarker of pembrolizumab efficacy for patients affected by advanced non-small cell lung cancer overexpressing PD-L1: results of the exploratory "FoRECATT" study
Abstract
Background: Identifying the patients who may benefit the most from immune checkpoints inhibitors remains a great challenge for clinicians. Here we investigate on blood serum amyloid A (SAA) as biomarker of response to upfront pembrolizumab in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
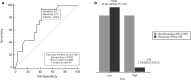
Methods: Patients with PD-L1 ≥ 50% receiving upfront pembrolizumab (P cohort) and with PD-L1 0-49% treated with chemotherapy (CT cohort) were evaluated for blood SAA and radiological response at baseline and every 9 weeks. Endpoints were response rate (RR) according to RECIST1.1, progression-free (PFS) and overall survival (OS). The most accurate SAA cut-off to predict response was established with ROC analysis in the P cohort.
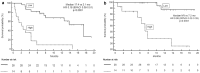
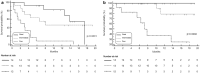
Results: In the P Cohort (n = 42), the overall RR was 38%. After a median follow-up of 18.5 months (mo), baseline SAA ≤ the ROC-derived cut-off (29.9 mg/L; n = 28/42.67%) was significantly associated with higher RR (53.6 versus 7.1%; OR15, 95% CI 1.72-130.7, p = 0.009), longer PFS (17.4 versus 2.1 mo; p < 0.0001) and OS (not reached versus 7.2mo; p < 0.0001) compared with SAA > 29.9 mg/L. In multivariate analysis, low SAA positively affects PFS (p = 0.001) and OS (p = 0.048) irrespective of ECOG PS, number of metastatic sites and pleural effusion. SAA monitoring (n = 40) was also significantly associated with survival endpoints: median PFS 17.4 versus 2.1 mo and median OS not reached versus 7.2 mo when SAA remained low (n = 14) and high (n = 12), respectively. In the CT Cohort (n = 30), RR was not affected by SAA level (p > 0.05) while low SAA at baseline (n = 17) was associated with better PFS (HR 0.38, 95% CI 0.16-0.90, p = 0.006) and OS (HR 0.25, 95% CI 0.09-0.67, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Low SAA predicts good survival outcomes irrespective of treatment for advanced NSCLC patients and higher likelihood of response to upfront pembrolizumab only. The strong prognostic value might be exploited to easily identify patients most likely to benefit from immunotherapy. A further study (FoRECATT-2) is ongoing to confirm results in a larger sample size and to investigate the effect of SAA on immune response in vitro assays.
Keywords: Biomarker of response; NSCLC; Pembrolizumab; Predictive/prognostic factors to immune-checkpoint inhibitors; Serum amyloid A.
Conflict of interest statement
V.D.N. received speakers’ fee by Astrazeneca, MSD, BMS, Istituto Gentili, Boehringer Ingelheim. V.D.N. received grant consultancies by Astrazeneca, MSD, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim and travels’ fee from MSD and Boehringer Ingelheim. V.D.N. received institutional research grants from Roche. E.B. received speakers’ and travels’ fee from MSD, Astra-Zeneca, Celgene, Pfizer, Helsinn, Eli-Lilly, BMS, Novartis and Roche. E.B received consultant’s fee from Roche, Pfizer. E.B. received institutional research grants from Astra-Zeneca, Roche.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcomes to first-line pembrolizumab in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and very high PD-L1 expression.Ann Oncol. 2019 Oct 1;30(10):1653-1659. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz288. Ann Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31435660
-
Real-World Efficacy of First-Line Pembrolizumab in Patients With Advanced or Recurrent Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and High PD-L1 Tumor Expression.Clin Lung Cancer. 2020 Sep;21(5):e366-e379. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2020.02.017. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Clin Lung Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32199806
-
Association between metastatic sites and first-line pembrolizumab treatment outcome for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with high PD-L1 expression: a retrospective multicenter cohort study.Invest New Drugs. 2020 Feb;38(1):211-218. doi: 10.1007/s10637-019-00882-5. Epub 2019 Nov 30. Invest New Drugs. 2020. PMID: 31784866
-
The relationship between blood-based tumor mutation burden level and efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2021 Nov 13;21(1):1220. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08924-z. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34774004 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical benefit of pembrolizumab in treatment of first line non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical characteristics.BMC Cancer. 2023 May 19;23(1):458. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10959-3. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37202730 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Potential biomarkers for immunotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023 Sep;42(3):661-675. doi: 10.1007/s10555-022-10074-y. Epub 2023 May 1. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023. PMID: 37121931 Review.
-
Molecular and translational biology of the blood-based VeriStrat® proteomic test used in cancer immunotherapy treatment guidance.J Mass Spectrom Adv Clin Lab. 2023 Nov 20;30:51-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsacl.2023.11.001. eCollection 2023 Nov. J Mass Spectrom Adv Clin Lab. 2023. PMID: 38074293 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic literature review of real-world evidence on overall survival in cancer patients before and after the approval of anti-PD-(L)1 therapy.Front Oncol. 2025 Aug 4;15:1615795. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1615795. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40831930 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world performance of blood-based proteomic profiling in first-line immunotherapy treatment in advanced stage non-small cell lung cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Oct;9(10):e002989. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002989. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34706885 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic inflammation is a determinant of outcomes of CD40 agonist-based therapy in pancreatic cancer patients.JCI Insight. 2021 Mar 8;6(5):e145389. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.145389. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 33497362 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Rittmeyer A, Barlesi F, Waterkamp D, et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, openlabel, multicentre randomised controlled trial. The Lancet. 2017;389(10066):255–265. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32517-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous