Metformin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and cell pyroptosis via AMPK/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway
- PMID: 33232283
- PMCID: PMC7762510
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.202143
Metformin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and cell pyroptosis via AMPK/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway
Abstract
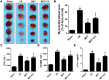
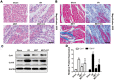
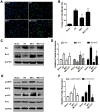
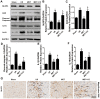
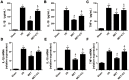
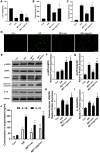
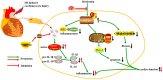
Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is a life-threatening vascular emergency following myocardial infarction. Our previous study showed cardioprotective effects of metformin against myocardial I/R injury. In this study, we further examined the involvement of AMPK mediated activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in this cardioprotective effect of metformin. Myocardial I/R injury was simulated in a rat heart Langendorff model and neonatal rat ventricle myocytes (NRVMs) were subjected to hypoxi/reoxygenation (H/R) to establish an in vitro model. Outcome measures included myocardial infarct size, hemodynamic monitoring, myocardial tissue injury, myocardial apoptotic index and the inflammatory response. myocardial infarct size and cardiac enzyme activities. First, we found that metformin postconditioning can not only significantly alleviated myocardial infarct size, attenuated cell apoptosis, and inhibited myocardial fibrosis. Furthermore, metformin activated phosphorylated AMPK, decreased pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β, and decreased NLRP3 inflammasome activation. In isolated NRVMs metformin increased cellular viability, decreased LDH activity and inhibited cellular apoptosis and inflammation. Importantly, inhibition of AMPK phosphorylation by Compound C (CC) resulted in decreased survival of cardiomyocytes mainly by inducing the release of inflammatory cytokines and increasing NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Finally, in vitro studies revealed that the NLRP3 activator nigericin abolished the anti-inflammatory effects of metformin in NRVMs, but it had little effect on AMPK phosphorylation. Collectively, our study confirmed that metformin exerts cardioprotective effects by regulating myocardial I/R injury-induced inflammatory response, which was largely dependent on the enhancement of the AMPK pathway, thereby suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
Keywords: APMK; NLRP3; metformin; myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury; pyroptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Tamis-Holland JE, Jneid H, Reynolds HR, Agewall S, Brilakis ES, Brown TM, Lerman A, Cushman M, Kumbhani DJ, Arslanian-Engoren C, Bolger AF, Beltrame JF, and American Heart Association Interventional Cardiovascular Care Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology, and Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention, and Council on Quality of Care and Outcomes Research. Contemporary diagnosis and management of patients with myocardial infarction in the absence of obstructive coronary artery disease: a scientific statement from the American heart association. Circulation. 2019; 139:e891–908. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000670 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

