Skin Manifestations Associated with COVID-19: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 33232965
- PMCID: PMC7801998
- DOI: 10.1159/000512932
Skin Manifestations Associated with COVID-19: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) is an ongoing global pandemic caused by the "severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2" (SARS-CoV-2), which was isolated for the first time in Wuhan (China) in December 2019. Common symptoms include fever, cough, fatigue, dyspnea and hypogeusia/hyposmia. Among extrapulmonary signs associated with COVID-19, dermatological manifestations have been increasingly reported in the last few months.
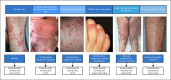
Summary: The polymorphic nature of COVID-19-associated cutaneous manifestations led our group to propose a classification, which distinguishes the following six main clinical patterns: (i) urticarial rash, (ii) confluent erythematous/maculopapular/morbilliform rash, (iii) papulovesicular exanthem, (iv) chilblain-like acral pattern, (v) livedo reticularis/racemosa-like pattern, (vi) purpuric "vasculitic" pattern. This review summarizes the current knowledge on COVID-19-associated cutaneous manifestations, focusing on clinical features and therapeutic management of each category and attempting to give an overview of the hypothesized pathophysiological mechanisms of these conditions.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cutaneous manifestations; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2020 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Galván Casas C, Català A, Carretero Hernández G, Rodríguez-Jiménez P, Fernández-Nieto D, Rodríguez-Villa Lario A, et al. Classification of the cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: a rapid prospective nationwide consensus study in Spain with 375 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2020 Jul;183((1)):71–7. - PMC - PubMed

