Low Intensity, Transcranial, Alternating Current Stimulation Reduces Migraine Attack Burden in a Home Application Set-Up: A Double-Blinded, Randomized Feasibility Study
- PMID: 33233400
- PMCID: PMC7700448
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci10110888
Low Intensity, Transcranial, Alternating Current Stimulation Reduces Migraine Attack Burden in a Home Application Set-Up: A Double-Blinded, Randomized Feasibility Study
Abstract
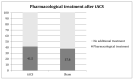
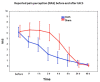
Background: Low intensity, high-frequency transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) applied over the motor cortex decreases the amplitude of motor evoked potentials. This double-blind, placebo-controlled parallel group study aimed to test the efficacy of this method for acute management of migraines. Methods: The patients received either active (0.4 mA, 140 Hz) or sham stimulation for 15 min over the visual cortex with the number of terminated attacks two hours post-stimulation as the primary endpoint, as a home therapy option. They were advised to treat a maximum of five migraine attacks over the course of six weeks. Results: From forty patients, twenty-five completed the study, sixteen in the active and nine in the sham group with a total of 102 treated migraine attacks. The percentage of terminated migraine attacks not requiring acute rescue medication was significantly higher in the active (21.5%) than in the sham group (0%), and the perceived pain after active stimulation was significantly less for 2-4 h post-stimulation than after sham stimulation. Conclusion: tACS over the visual cortex has the potential to terminate migraine attacks. Nevertheless, the high drop-out rate due to compliance problems suggests that this method is impeded by its complexity and time-consuming setup.
Keywords: acute treatment; migraine; tACS; transcranial stimulation; visual cortex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lipton R.B., Dodick D.W., Silberstein S.D., Saper J.R., Aurora S.K., Pearlman S.H., Fischell R.E., Ruppel P.L., Goadsby P.J. Single-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation for acute treatment of migraine with aura: A randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, sham-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:373–380. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70054-5. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

