An Original ELISA-Based Multiplex Method for the Simultaneous Detection of 5 SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibodies Directed against Different Antigens
- PMID: 33233405
- PMCID: PMC7700260
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9113752
An Original ELISA-Based Multiplex Method for the Simultaneous Detection of 5 SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibodies Directed against Different Antigens
Abstract
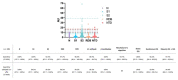
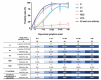
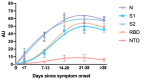
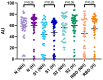
Strategies to detect SARS-CoV-2 are increasingly being developed. Among them, serological methods have been developed. Nevertheless, although these may present an interesting clinical performance, they are often directed against only one antigen. This study aims at evaluating the clinical performance of an innovative multiplex immunoassay (i.e., CoViDiag assay) detecting simultaneously the presence of antibodies directed against N, S1, S2, RBD and NTD antigens. Sensitivity was evaluated in 135 samples obtained from 94 rRT-PCR confirmed coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. Non-SARS-CoV-2 sera (n = 132) collected before the COVID-19 pandemic with potential cross-reactions to the SARS-CoV-2 immunoassay were included in the specificity analysis. The antibody signature was also studied in hospitalized and non-hospitalized patients. The specificity of the CoViDiag assay was excellent for all antibodies (99.2 to 100%) using adapted cut-offs. None of the false positive samples were positive for more than one antibody. The sensitivity obtained from samples collected 14 days since symptom onset varied from 92.0 to 100.0% depending on the antibody considered. Among samples collected more than 14 days after symptom onset, 12.8, 66.3, 3.5, 9.3, 5.8 and 2.3% were positive for 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 or 0 antibodies, respectively. A trend toward higher antibody titers was observed in hospitalized patient in the early days since symptom onset. However, no significant difference was observed compared to non-hospitalized patients after 14 days since symptom onset. The clinical performance of the CoViDiag 5 IgG assay is sufficient to recommend its use for the detection and the characterization of the antibody signature following SARS-CoV-2 infection. The combination of several antigens in the same test improves the overall specificity and sensitivity of the test. Further research is needed to investigate whether this strategy may be of interest to identify severe disease outcome in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; kinetics; multiplex; serology.
Conflict of interest statement
Among the authors, J.D. is CEO and founder of QUALIblood s.a., a contract research organization manufacturing the DP-Filter, is co-inventor of the DP-Filter (patent application number: PCT/ET2019/052903) and reports personal fees from Daiichi-Sankyo, Mithra Pharmaceuticals, Stago, Roche and Roche Diagnostics outside the submitted work. The other authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An original multiplex method to assess five different SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020 Dec 21;59(5):971-978. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2020-1652. Print 2021 Apr 27. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 33554567
-
Evaluation of a Multiplex Bead Assay against Single-Target Assays for Detection of IgG Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0105422. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01054-22. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35647696 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a Pan-Immunoglobulin Assay Quantifying Antibodies Directed against the Receptor Binding Domain of the SARS-CoV-2 S1-Subunit of the Spike Protein: A Population-Based Study.J Clin Med. 2020 Dec 9;9(12):3989. doi: 10.3390/jcm9123989. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33317059 Free PMC article.
-
Serological testing for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in clinical practice: A comparative diagnostic accuracy study.Allergy. 2022 Jul;77(7):2090-2103. doi: 10.1111/all.15206. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Allergy. 2022. PMID: 34986501 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplex assays for the identification of serological signatures of SARS-CoV-2 infection: an antibody-based diagnostic and machine learning study.Lancet Microbe. 2021 Feb;2(2):e60-e69. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30197-X. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Lancet Microbe. 2021. PMID: 33521709 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous measurement of the antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 and its multiple variants by a phage display mediated immuno-multiplex quantitative PCR-based assay.Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 22;13:968036. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.968036. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36071962 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitively detecting antigen of SARS-CoV-2 by NIR-II fluorescent nanoparticles.Nano Res. 2022;15(8):7313-7319. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4351-1. Epub 2022 May 10. Nano Res. 2022. PMID: 35571588 Free PMC article.
-
Binding and neutralizing abilities of antibodies towards SARS-CoV-2 S2 domain.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Nov 30;18(5):2055373. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2055373. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022. PMID: 35417303 Free PMC article.
-
A multiplex serological assay for the characterization of IgG immune response to SARS-CoV-2.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 13;17(1):e0262311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262311. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35025936 Free PMC article.
-
VLP-ELISA for the Detection of IgG Antibodies against Spike, Envelope, and Membrane Antigens of SARS-CoV-2 in Indian Population.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Mar 27;11(4):743. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11040743. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37112655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report—Weekly Evaluation Update 3 November 2020. [(accessed on 3 November 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update---....
-
- Bohn M.K., Lippi G., Horvath A., Sethi S., Koch D., Ferrari M., Wang C.B., Mancini N., Steele S., Adeli K. Molecular, serological, and biochemical diagnosis and monitoring of COVID-19: IFCC taskforce evaluation of the latest evidence. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020;58:1037–1052. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2020-0722. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

