Emerging Kinase Therapeutic Targets in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Pancreatic Cancer Desmoplasia
- PMID: 33233470
- PMCID: PMC7700673
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21228823
Emerging Kinase Therapeutic Targets in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Pancreatic Cancer Desmoplasia
Abstract
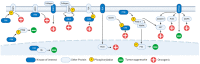
Kinase drug discovery represents an active area of therapeutic research, with previous pharmaceutical success improving patient outcomes across a wide variety of human diseases. In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), innovative pharmaceutical strategies such as kinase targeting have been unable to appreciably increase patient survival. This may be due, in part, to unchecked desmoplastic reactions to pancreatic tumors. Desmoplastic stroma enhances tumor development and progression while simultaneously restricting drug delivery to the tumor cells it protects. Emerging evidence indicates that many of the pathologic fibrotic processes directly or indirectly supporting desmoplasia may be driven by targetable protein tyrosine kinases such as Fyn-related kinase (FRK); B lymphoid kinase (BLK); hemopoietic cell kinase (HCK); ABL proto-oncogene 2 kinase (ABL2); discoidin domain receptor 1 kinase (DDR1); Lck/Yes-related novel kinase (LYN); ephrin receptor A8 kinase (EPHA8); FYN proto-oncogene kinase (FYN); lymphocyte cell-specific kinase (LCK); tec protein kinase (TEC). Herein, we review literature related to these kinases and posit signaling networks, mechanisms, and biochemical relationships by which this group may contribute to PDAC tumor growth and desmoplasia.
Keywords: SRC family kinases; desmoplasia; drug discovery; fibrosis; kinase therapy; pancreatic cancer; transcription factors.
Conflict of interest statement
T.T. and F.N. are employed by PamGene International B.V. The remaining authors have declared that no conflicts of interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Orth M., Metzger P., Gerum S., Mayerle J., Schneider G., Belka C., Schnurr M., Lauber K. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Biological hallmarks, current status, and future perspectives of combined modality treatment approaches. Radiat. Oncol. 2019;14:1–20. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1345-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

