Is Ultrasound an Accurate Alternative for Mammography in Breast Cancer Screening in an Asian Population? A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33233479
- PMCID: PMC7700617
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics10110985
Is Ultrasound an Accurate Alternative for Mammography in Breast Cancer Screening in an Asian Population? A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
In Asian countries, ultrasound has been proposed as a possible alternative for mammography in breast cancer screening because of its superiority in dense breasts, accessibility and low costs. This research aimed to meta-analyze the evidence for the diagnostic performance of ultrasound compared to mammography for breast cancer screening in Asian women. PubMed, Web of Science, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure databases were searched for studies that concurrently compared mammography and ultrasound in 2000-2019. Data extraction and risk of bias were performed according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA) statement. The primary outcome was the sensitivity and specificity. Bivariate random models were used to generate pooled estimates of diagnostic parameters and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI). In total, 4424 studies were identified of which six studies met the inclusion criteria with a sample size of 124,425 women. The pooled mean prevalence of the included studies was 3.7‱ (range: 1.2-5.7‱). The pooled sensitivity of mammography was significantly higher than that of ultrasound (0.81 [95% CI 0.71-0.88] versus 0.65 [95% CI 0.58-0.72], p = 0.03), but no significant differences were found in specificity (0.98 [95% CI: 0.94-1.00] versus 0.99 [95% CI: 0.97-1.00], p = 0.65). In conclusion, based on the currently available data on sensitivity alone, there is no indication that ultrasound can replace mammography in breast cancer screening in Asian women.
Keywords: breast neoplasms; mammography; mass screening; meta-analysis; ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
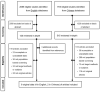
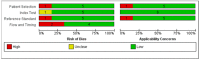

References
-
- Sung H., Rosenberg P.S., Chen W.-Q., Hartman M., Lim W.-Y., Chia K.S., Mang O.W.-K., Chiang C.-J., Kang D., Ngan R.K.-C., et al. Female Breast Cancer Incidence Among Asian and Western Populations: More Similar Than Expected. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015;107:djv107. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moss S.M., Wale C., A Smith R., Evans A., Cuckle H., Duffy S.W. Effect of mammographic screening from age 40 years on breast cancer mortality in the UK Age trial at 17 years’ follow-up: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:1123–1132. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00128-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

