Ferroptosis Mechanisms Involved in Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 33233496
- PMCID: PMC7699575
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21228765
Ferroptosis Mechanisms Involved in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
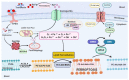
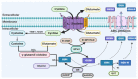
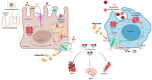
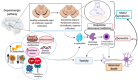
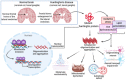
Ferroptosis is a type of cell death that was described less than a decade ago. It is caused by the excess of free intracellular iron that leads to lipid (hydro) peroxidation. Iron is essential as a redox metal in several physiological functions. The brain is one of the organs known to be affected by iron homeostatic balance disruption. Since the 1960s, increased concentration of iron in the central nervous system has been associated with oxidative stress, oxidation of proteins and lipids, and cell death. Here, we review the main mechanisms involved in the process of ferroptosis such as lipid peroxidation, glutathione peroxidase 4 enzyme activity, and iron metabolism. Moreover, the association of ferroptosis with the pathophysiology of some neurodegenerative diseases, namely Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's diseases, has also been addressed.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; GSH; Huntington’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; cell death; ferroptosis; glutathione peroxidase 4; iron metabolism; neurodegenerative diseases; system xc−.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Galluzzi L., Vitale I., Aaronson S.A., Abrams J.M., Adam D., Agostinis P., Alnemri E.S., Altucci L., Amelio I., Andrews D.W., et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:486–541. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Levy D., de Melo T.C., Oliveira B.A., Paz J.L., de Freitas F.A., Reichert C.O., Rodrigues A., Bydlowski S.P. 7-Ketocholesterol and cholestane-triol increase expression of SMO and LXRα signaling pathways in a human breast cancer cell line. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018;19 doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2018.12.008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

