The Search for New Anticonvulsants in a Group of (2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)(phenyl)Acetamides with Hybrid Structure-Synthesis and In Vivo/In Vitro Studies
- PMID: 33233618
- PMCID: PMC7699745
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21228780
The Search for New Anticonvulsants in a Group of (2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)(phenyl)Acetamides with Hybrid Structure-Synthesis and In Vivo/In Vitro Studies
Abstract
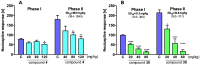
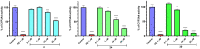
Epilepsy belongs to the most common and debilitating neurological disorders with multifactorial pathophysiology and a high level of drug resistance. Therefore, with the aim of searching for new, more effective, and/or safer therapeutics, we discovered a focused series of original hybrid pyrrolidine-2,5-dione derivatives with potent anticonvulsant properties. We applied an optimized coupling reaction yielding several hybrid compounds that showed broad-spectrum activity in widely accepted animal seizure models, namely, the maximal electroshock (MES) test and the psychomotor 6 Hz (32 mA) seizure model in mice. The most potent anticonvulsant activity and favorable safety profile was demonstrated for compound 30 (median effective dose (ED50) MES = 45.6 mg/kg, ED50 6 Hz (32 mA) = 39.5 mg/kg, median toxic dose (TD50) (rotarod test) = 162.4 mg/kg). Anticonvulsant drugs often show activity in pain models, and compound 30 was also proven effective in the formalin test of tonic pain, the capsaicin-induced pain model, and the oxaliplatin (OXPT)-induced neuropathic pain model in mice. Our studies showed that the most plausible mechanism of action of 30 involves inhibition of calcium currents mediated by Cav1.2 (L-type) channels. Importantly, 30 revealed high metabolic stability on human liver microsomes, negligible hepatotoxicity, and relatively weak inhibition of CYP3A4, CYP2D6, and CYP2C9 isoforms of cytochrome P450, compared to reference compounds. The promising in vivo activity profile and drug-like properties of compound 30 make it an interesting candidate for further preclinical development.
Keywords: absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, toxicity (ADME-Tox) properties; anticonvulsant activity; antinociceptive activity; hybrid molecules; in vitro binding/functional studies; pyrrolidine-2,5-dione.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of New Compounds with Anticonvulsant and Antinociceptive Properties in a Group of 3-substituted (2,5-dioxo-pyrrolidin-1-yl)(phenyl)-Acetamides.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 3;22(23):13092. doi: 10.3390/ijms222313092. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884898 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of new hybrid anticonvulsants derived from N-benzyl-2-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)propanamide and 2-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butanamide derivatives.Bioorg Med Chem. 2015 May 15;23(10):2548-61. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.03.038. Epub 2015 Mar 21. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25868743
-
Multitargeted Compounds Derived from (2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)(phenyl)-Acetamides as Candidates for Effective Anticonvulsant and Antinociceptive Agents.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020 Jul 1;11(13):1996-2008. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00257. Epub 2020 Jun 17. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32479058
-
Novel Hybrid Anticonvulsants Derived from Pyrrolidine-2,5-dione Scaffold with Broad Spectrum of Activity in the Preclinical Studies.Curr Top Med Chem. 2017;17(8):858-874. doi: 10.2174/1568026616666160927153025. Curr Top Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27697054 Review.
-
α-Substituted Lactams and Acetamides: Ion Channel Modulators that Show Promise in Treating Drug-resistant Epilepsy.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2020;20(2):79-87. doi: 10.2174/1871524920666200510005458. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32386500 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Novel Alaninamide Derivatives with Anticonvulsant Activity and Favorable Safety Profiles in Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 12;25(18):9861. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189861. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337345 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive and Antiallodynic Activity of Some 3-(3-Methylthiophen-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione Derivatives in Mouse Models of Tonic and Neuropathic Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 6;23(7):4057. doi: 10.3390/ijms23074057. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409413 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Alaninamide Derivatives with Drug-like Potential for Development as Antiseizure and Antinociceptive Therapies─In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024 Jun 5;15(11):2198-2222. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00013. Epub 2024 May 14. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38741575 Free PMC article.
-
New Phenylglycinamide Derivatives with Hybrid Structure as Candidates for New Broad-Spectrum Anticonvulsants.Cells. 2022 Jun 7;11(12):1862. doi: 10.3390/cells11121862. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35740990 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of New Compounds with Anticonvulsant and Antinociceptive Properties in a Group of 3-substituted (2,5-dioxo-pyrrolidin-1-yl)(phenyl)-Acetamides.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 3;22(23):13092. doi: 10.3390/ijms222313092. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Media Centre. Epilepsy. Fact Sheet No. 999. May 2015. [(accessed on 19 November 2020)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs999/en/
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

