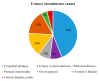
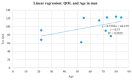
The Impact of Urinary Incontinence on Quality of Life: A Cross-Sectional Study in the Metropolitan City of Naples
- PMID: 33233663
- PMCID: PMC7709681
- DOI: 10.3390/geriatrics5040096
The Impact of Urinary Incontinence on Quality of Life: A Cross-Sectional Study in the Metropolitan City of Naples
Abstract
Urinary incontinence is a hygienic and psychosocial problem that often brings people to restrict their social life and to experience depression. The main aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of urinary incontinence on quality of life among residents of the Metropolitan City of Naples, Italy, using a newly designed multidimensional questionnaire. The secondary objective was to find which variables affect the quality of life and symptom severity in these patients. To do so, a sample composed of twenty-eight patients was recruited in a multicentre cross-sectional study. Most of the participants had a mild impairment (60%) concerning social life and self-perception, especially those whose education was above the primary level (p = 0.036) and those who followed a pelvic floor rehabilitation program (p = 0.002). Overflow urinary incontinence was associated with a greater deterioration in the aspirational and occupational domain (p = 0.044). Symptom severity was worse in those who had comorbidities (p = 0.038), who had a high body mass index (p = 0.008) or who used diuretics (p = 0.007). In conclusion, our results suggest that there is a significant impairment of quality of life in patients who have only primary education and who follow a pelvic floor rehabilitation program.
Keywords: chronic illness; incontinence; patient-centered care; quality of life; questionnaire; survey; symptom perception.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Coexisting Pelvic Floor Disorders on Fecal Incontinence Quality of Life Scores: A Prospective, Survey-Based Study.Dis Colon Rectum. 2015 Nov;58(11):1091-7. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000000459. Dis Colon Rectum. 2015. PMID: 26445183
-
Effectiveness of a pelvic floor muscle exercise program on urinary incontinence following childbirth.Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2005 May;3(5):103-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-6988.2005.00023.x. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2005. PMID: 21631746
-
The effect of major depression on quality of life after surgery for stress urinary incontinence: a secondary analysis of the Trial of Midurethral Slings.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Oct;215(4):455.e1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2016.04.039. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016. PMID: 27133008 Clinical Trial.
-
Validity of utility measures for women with pelvic organ prolapse.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Jan;218(1):119.e1-119.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.09.022. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 28988907
-
[Impact of biofeedback probes used in the self-rehabilitation of pelvic floor muscles in women with stress urinary incontinence. Literature review].Prog Urol. 2021 Jun;31(7):385-391. doi: 10.1016/j.purol.2021.01.006. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Prog Urol. 2021. PMID: 33583738 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Impact of Different Types of Physical Exercises for the Management of Older Women with Urinary Incontinence: A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials.J Clin Med. 2025 May 14;14(10):3425. doi: 10.3390/jcm14103425. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40429419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of a Smart Diaper Sensor on Incontinence-Associated Dermatitis Afflicting a Sedentary Patient with Cognitive Impairment.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 7;14(7):2526. doi: 10.3390/jcm14072526. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40217977 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Impact on Quality of Life Due to Urinary Incontinence Among Palestinian Women: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2024 Apr 8;16(4):e57813. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57813. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38721207 Free PMC article.
-
Patient Reported Outcomes and Treatment-Associated Complications as a Consideration in Selecting Localized Prostate Cancer Management.Res Rep Urol. 2025 Jun 12;17:195-210. doi: 10.2147/RRU.S386383. eCollection 2025. Res Rep Urol. 2025. PMID: 40528834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing Quality of Life Among Women with Urinary Incontinence-Medical, Psychological, and Sociodemographic Determinants.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 8;14(14):4839. doi: 10.3390/jcm14144839. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40725531 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrams P., Cardozo L., Fall M., Griffiths D., Rosier P., Ulmsten U., Van Kerrebroeck P., Victor A., Wein A.J. The standardisation of terminology in lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardisation sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Urology. 2003;61:37–49. doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(02)02243-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Price N., Currie I. Urinary incontinence in women: Diagnosis and management. Practitioner. 2010;254:27–33. - PubMed
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Urinary Incontinence in Women: Management [CG171] [(accessed on 21 September 2016)];2015 Available online: http://tinyurl.com/jcmyvyl.
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Men: Management [CG97] [(accessed on 21 September 2016)];2015 Available online: http://tinyurl.com/z33bgyn. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources