The Impact of Urinary Incontinence on Quality of Life: A Cross-Sectional Study in the Metropolitan City of Naples
- PMID: 33233663
- PMCID: PMC7709681
- DOI: 10.3390/geriatrics5040096
The Impact of Urinary Incontinence on Quality of Life: A Cross-Sectional Study in the Metropolitan City of Naples
Abstract
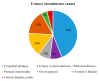
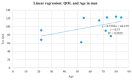
Urinary incontinence is a hygienic and psychosocial problem that often brings people to restrict their social life and to experience depression. The main aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of urinary incontinence on quality of life among residents of the Metropolitan City of Naples, Italy, using a newly designed multidimensional questionnaire. The secondary objective was to find which variables affect the quality of life and symptom severity in these patients. To do so, a sample composed of twenty-eight patients was recruited in a multicentre cross-sectional study. Most of the participants had a mild impairment (60%) concerning social life and self-perception, especially those whose education was above the primary level (p = 0.036) and those who followed a pelvic floor rehabilitation program (p = 0.002). Overflow urinary incontinence was associated with a greater deterioration in the aspirational and occupational domain (p = 0.044). Symptom severity was worse in those who had comorbidities (p = 0.038), who had a high body mass index (p = 0.008) or who used diuretics (p = 0.007). In conclusion, our results suggest that there is a significant impairment of quality of life in patients who have only primary education and who follow a pelvic floor rehabilitation program.
Keywords: chronic illness; incontinence; patient-centered care; quality of life; questionnaire; survey; symptom perception.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abrams P., Cardozo L., Fall M., Griffiths D., Rosier P., Ulmsten U., Van Kerrebroeck P., Victor A., Wein A.J. The standardisation of terminology in lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardisation sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Urology. 2003;61:37–49. doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(02)02243-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Price N., Currie I. Urinary incontinence in women: Diagnosis and management. Practitioner. 2010;254:27–33. - PubMed
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Urinary Incontinence in Women: Management [CG171] [(accessed on 21 September 2016)];2015 Available online: http://tinyurl.com/jcmyvyl.
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Men: Management [CG97] [(accessed on 21 September 2016)];2015 Available online: http://tinyurl.com/z33bgyn. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources