Automatic Stomatal Segmentation Based on Delaunay-Rayleigh Frequency Distance
- PMID: 33233729
- PMCID: PMC7699937
- DOI: 10.3390/plants9111613
Automatic Stomatal Segmentation Based on Delaunay-Rayleigh Frequency Distance
Abstract
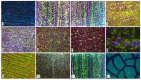
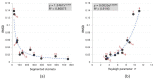
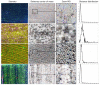
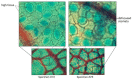
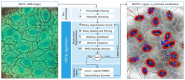
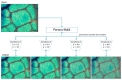
The CO2 and water vapor exchange between leaf and atmosphere are relevant for plant physiology. This process is done through the stomata. These structures are fundamental in the study of plants since their properties are linked to the evolutionary process of the plant, as well as its environmental and phytohormonal conditions. Stomatal detection is a complex task due to the noise and morphology of the microscopic images. Although in recent years segmentation algorithms have been developed that automate this process, they all use techniques that explore chromatic characteristics. This research explores a unique feature in plants, which corresponds to the stomatal spatial distribution within the leaf structure. Unlike segmentation techniques based on deep learning tools, we emphasize the search for an optimal threshold level, so that a high percentage of stomata can be detected, independent of the size and shape of the stomata. This last feature has not been reported in the literature, except for those results of geometric structure formation in the salt formation and other biological formations.
Keywords: Delaunay-Rayleigh frequency; image segmentation; stomatal segmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
A Deep Learning-Based Method for Automatic Assessment of Stomatal Index in Wheat Microscopic Images of Leaf Epidermis.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Sep 3;12:716784. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.716784. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34539710 Free PMC article.
-
Microscope image based fully automated stomata detection and pore measurement method for grapevines.Plant Methods. 2017 Nov 8;13:94. doi: 10.1186/s13007-017-0244-9. eCollection 2017. Plant Methods. 2017. PMID: 29151841 Free PMC article.
-
A Deep Learning Method for Fully Automatic Stomatal Morphometry and Maximal Conductance Estimation.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Dec 2;12:780180. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.780180. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34925424 Free PMC article.
-
[Coordination effect between vapor water loss through plant stomata and liquid water supply in soil-plant-atmosphere continuum (SPAC): a review].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2008 Sep;19(9):2067-73. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 19102325 Review. Chinese.
-
Application of deep learning for the analysis of stomata: a review of current methods and future directions.J Exp Bot. 2024 Nov 15;75(21):6704-6718. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae207. J Exp Bot. 2024. PMID: 38716775 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fanourakis D., Aliniaeifard S., Sellin A., Giday H., Körner O., Nejad A.R., Delis C., Bouranis D., Koubouris G., Kambourakis E., et al. Stomatal behavior following mid- or long-term exposure to high relative air humidity: A review. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020;153:92–105. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.05.024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhu Z., Piao S., Myneni R.B., Huang M., Zeng Z., Canadell J.G., Ciais P., Sitch S., Friedlingstein P., Arneth A., et al. Greening of the Earth and its drivers. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016;6:791–795. doi: 10.1038/nclimate3004. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

