The Hippo Pathway in Liver Homeostasis and Pathophysiology
- PMID: 33234023
- PMCID: PMC8594752
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-030420-105050
The Hippo Pathway in Liver Homeostasis and Pathophysiology
Abstract
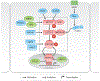
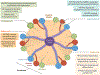
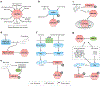
Studies of the regenerative capacity of the liver have converged on the Hippo pathway, a serine/threonine kinase cascade discovered in Drosophila and conserved from unicellular organisms to mammals. Genetic studies of mouse and rat livers have revealed that the Hippo pathway is a key regulator of liver size, regeneration, development, metabolism, and homeostasis and that perturbations in the Hippo pathway can lead to the development of common liver diseases, such as fatty liver disease and liver cancer. In turn, pharmacological targeting of the Hippo pathway may be utilized to boost regeneration and to prevent the development and progression of liver diseases. We review current insights provided by the Hippo pathway into liver pathophysiology. Furthermore, we present a path forward for future studies to understand how newly identified components of the Hippo pathway may control liver physiology and how the Hippo pathway is regulated in the liver.
Keywords: Hippo pathway; YAP/TAZ; fatty liver disease; liver cancer; metabolism; regeneration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Hippo signaling pathway in liver regeneration and tumorigenesis.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2015 Jan;47(1):46-52. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmu106. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2015. PMID: 25476204 Review.
-
Hippo pathway coactivators Yap and Taz are required to coordinate mammalian liver regeneration.Exp Mol Med. 2018 Jan 5;50(1):e423. doi: 10.1038/emm.2017.205. Exp Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29303509 Free PMC article.
-
The Hippo Pathway: Biology and Pathophysiology.Annu Rev Biochem. 2019 Jun 20;88:577-604. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-013118-111829. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30566373 Review.
-
The Hippo pathway in tissue homeostasis and regeneration.Protein Cell. 2017 May;8(5):349-359. doi: 10.1007/s13238-017-0371-0. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Protein Cell. 2017. PMID: 28130761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging evidence on the role of the Hippo/YAP pathway in liver physiology and cancer.J Hepatol. 2015 Dec;63(6):1491-501. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.07.008. Epub 2015 Jul 28. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26226451 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the significance and potential mechanisms of hippo pathway-associated genes in prognosis of glioma patients.Discov Oncol. 2024 Oct 9;15(1):536. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01391-5. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39382606 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative liver transcriptome analysis in hamsters infected with food-borne trematodes Opisthorchis felineus, Opisthorchis viverrini, or Clonorchis sinensis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Dec 9;18(12):e0012685. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012685. eCollection 2024 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39652576 Free PMC article.
-
OPN-Mediated Crosstalk Between Hepatocyte E4BP4 and Hepatic Stellate Cells Promotes MASH-Associated Liver Fibrosis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Dec;11(47):e2405678. doi: 10.1002/advs.202405678. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39473081 Free PMC article.
-
ROS-induced cytosolic release of mitochondrial PGAM5 promotes colorectal cancer progression by interacting with MST3.Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 6;16(1):1406. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56444-2. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39915446 Free PMC article.
-
Hippo signaling pathway and respiratory diseases.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Apr 20;8(1):213. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01020-6. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35443749 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Michalopoulos GK, DeFrances MC. 1997. Liver regeneration. Science 276:60–66 - PubMed
-
- Higgins GM, Anderson RM. 1931. Experimental pathology of liver: restoration of liver in the white rat following partial surgical removal. Arch. Pathol 12:186–202
-
- Emre S, Umman V. 2011. Split liver transplantation: an overview. Transplant. Proc 43:884–87 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

