Association between serum lactate levels and mortality in patients with cardiogenic shock receiving mechanical circulatory support: a multicenter retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 33234107
- PMCID: PMC7687839
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-020-01785-7
Association between serum lactate levels and mortality in patients with cardiogenic shock receiving mechanical circulatory support: a multicenter retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the prognostic value of peak serum lactate and lactate clearance at several time points in cardiogenic shock treated with temporary mechanical circulatory support (MCS) using veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) or Impella CP®.
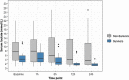
Methods: Serum lactate and clearance were measured before MCS and at 1 h, 6 h, 12 h, and 24 h post-MCS in 43 patients at four tertiary-care centers in Southern Brazil. Prognostic value was assessed by univariable and multivariable analysis and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for 30-day mortality.
Results: VA-ECMO was the most common MCS modality (58%). Serum lactate levels at all time points and lactate clearance after 6 h were associated with mortality on unadjusted and adjusted analyses. Lactate levels were higher in non-survivors at 6 h, 12 h, and 24 h after MCS. Serum lactate > 1.55 mmol/L at 24 h was the best single prognostic marker of 30-day mortality [area under the ROC curve = 0.81 (0.67-0.94); positive predictive value = 86%). Failure to improve serum lactate after 24 h was associated with 100% mortality.
Conclusions: Serum lactate was an important prognostic biomarker in cardiogenic shock treated with temporary MCS. Serum lactate and lactate clearance at 24 h were the strongest independent predictors of short-term survival.
Keywords: Cardiogenic shock; Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; Impella; Lactic acid; Mechanical circulatory support.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hernández G, Ospina-Tascón GA, Damiani LP, Estenssoro E, Dubin A, Hurtado J, et al. Effect of a resuscitation strategy targeting peripheral perfusion status vs serum lactate levels on 28-day mortality among patients with septic shock: the ANDROMEDA-SHOCK Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA - J Am Med Assoc. 2019;321:654–664. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.0071. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rigamonti F, Montecucco F, Boroli F, Rey F, Gencer B, Cikirikcioglu M, et al. The peak of blood lactate during the first 24 h predicts mortality in acute coronary syndrome patients under extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Int J Cardiol. 2016;221:741–745. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.07.065. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

