Microarray analysis identification of key pathways and interaction network of differential gene expressions during osteogenic differentiation
- PMID: 33234152
- PMCID: PMC7687700
- DOI: 10.1186/s40246-020-00293-1
Microarray analysis identification of key pathways and interaction network of differential gene expressions during osteogenic differentiation
Abstract
Background: Adult bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) are multipotent stem cells that can differentiate into three lineages. They are suitable sources for cell-based therapy and regenerative medicine applications. This study aims to evaluate the hub genes and key pathways of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) related to osteogenesis by bioinformatics analysis in three different days. The DEGs were derived from the three different days compared with day 0.
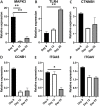
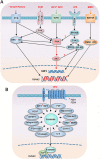
Results: Gene expression profiles of GSE37558 were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. A total of 4076 DEGs were acquired on days 8, 12, and 25. Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis showed that the non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated signaling pathway were commonly upregulated DEGs for all 3 days. KEGG pathway analysis indicated that the PI3K-Akt and focal adhesion were also commonly upregulated DEGs for all 3 days. Ten hub genes were identified by CytoHubba on days 8, 12, and 25. Then, we focused on the association of these hub genes with the Wnt pathways that had been enriched from the protein-protein interaction (PPI) by the Cytoscape plugin MCODE.
Conclusions: These findings suggested further insights into the roles of the PI3K/AKT and Wnt pathways and their association with osteogenesis. In addition, the stem cell microenvironment via growth factors, extracellular matrix (ECM), IGF1, IGF2, LPS, and Wnt most likely affect osteogenesis by PI3K/AKT.
Keywords: Bioinformatics analysis; Bone mesenchymal stem cells; Osteogenic differentiation; Protein-protein network.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics analysis and validation of RNA methylation-related genes in osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 Dec 20;739:150570. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150570. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 39181069
-
Bioinformatics analysis of the biological changes involved in the osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jul;24(14):7968-7978. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15429. Epub 2020 May 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32463168 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key genes and pathways associated with osteogenic differentiation of adipose stem cells.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Dec;233(12):9777-9785. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26943. Epub 2018 Aug 5. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30078218
-
Genomic Insights Into Statin Therapy: Differential Expression Analysis of Key Genes.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Jan;49(1 Pt B):102103. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.102103. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 37741602 Review.
-
Transcriptional networks controlling stromal cell differentiation.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Jul;22(7):465-482. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00357-7. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33837369 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Biomarkers That Modulate Osteogenic Differentiation in Mesenchymal Stem Cells Related to Inflammation and Immunity: A Bioinformatics-Based Comprehensive Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 31;15(9):1094. doi: 10.3390/ph15091094. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145314 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin Promotes Differentiation and Attenuates H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage of Osteoblasts via the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 21;13:829830. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.829830. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35387349 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling Pathways Driving MSC Osteogenesis: Mechanisms, Regulation, and Translational Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 4;26(3):1311. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031311. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39941080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the Smad2/3/4 signaling pathway in osteogenic differentiation regulation by ClC-3 chloride channels in MC3T3-E1 cells.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Jul 6;17(1):338. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03230-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35794618 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Analysis of Hypoxia-Induced Senescence of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Stem Cells Int. 2021 Aug 27;2021:5555590. doi: 10.1155/2021/5555590. eCollection 2021. Stem Cells Int. 2021. PMID: 34484348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- d'Aquino R, Graziano A, Sampaolesi M, Laino G, Pirozzi G, De Rosa A, et al. Human postnatal dental pulp cells co-differentiate into osteoblasts and endotheliocytes: a pivotal synergy leading to adult bone tissue formation. Cell death and differentiation. 2007;14(6):1162. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402121. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kirkham G, Cartmell S. Genes and proteins involved in the regulation of osteogenesis. Topics in tissue engineering. 2007;3:1–22.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

