Wnt signaling in breast cancer: biological mechanisms, challenges and opportunities
- PMID: 33234169
- PMCID: PMC7686704
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-020-01276-5
Wnt signaling in breast cancer: biological mechanisms, challenges and opportunities
Abstract
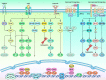
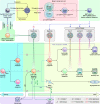
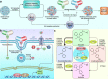
Wnt signaling is a highly conserved signaling pathway that plays a critical role in controlling embryonic and organ development, as well as cancer progression. Genome-wide sequencing and gene expression profile analyses have demonstrated that Wnt signaling is involved mainly in the processes of breast cancer proliferation and metastasis. The most recent studies have indicated that Wnt signaling is also crucial in breast cancer immune microenvironment regulation, stemness maintenance, therapeutic resistance, phenotype shaping, etc. Wnt/β-Catenin, Wnt-planar cell polarity (PCP), and Wnt-Ca2+ signaling are three well-established Wnt signaling pathways that share overlapping components and play different roles in breast cancer progression. In this review, we summarize the main findings concerning the relationship between Wnt signaling and breast cancer and provide an overview of existing mechanisms, challenges, and potential opportunities for advancing the therapy and diagnosis of breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Canonical/noncanonical Wnt signaling; Drug resistance; Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; Immune microenvironment; Phenotype shaping; Tumoral heterogeneity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
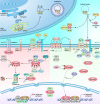
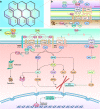
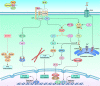

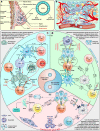

Similar articles
-
Role of the Wnt signaling pathway in the complex microenvironment of breast cancer and prospects for therapeutic potential (Review).Int J Oncol. 2025 May;66(5):36. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5742. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40145557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scope of Wnt signaling in the precise diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer.Drug Discov Today. 2023 Jul;28(7):103597. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103597. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Drug Discov Today. 2023. PMID: 37100166 Review.
-
Baicalein suppresses metastasis of breast cancer cells by inhibiting EMT via downregulation of SATB1 and Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Apr 18;10:1419-41. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S102541. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 27143851 Free PMC article.
-
γ-Tocotrienol reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer cells is associated with inhibition of canonical Wnt signalling.Cell Prolif. 2016 Aug;49(4):460-70. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12270. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Cell Prolif. 2016. PMID: 27323693 Free PMC article.
-
HOXD3 Plays a Critical Role in Breast Cancer Stemness and Drug Resistance.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(4):1737-1747. doi: 10.1159/000489249. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29698974
Cited by
-
Clinical Perspectives in Addressing Unsolved Issues in (Neo)Adjuvant Therapy for Primary Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 23;13(4):926. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040926. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evolving roles of Wnt signaling in stem cell proliferation and differentiation, the development of human diseases, and therapeutic opportunities.Genes Dis. 2023 Jul 22;11(3):101026. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.04.042. eCollection 2024 May. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 38292186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt3a is a promising target in colorectal cancer.Med Oncol. 2023 Jan 31;40(3):86. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-01958-2. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36719558 Review.
-
Overexpression of lncRNA MAPT-AS1 exacerbates cell proliferation and metastasis in breast cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Apr;11(4):835-847. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-719. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35571636 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Targets of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Where Do We Stand?Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 18;14(3):482. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030482. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158750 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeSantis CE, Ma J, Gaudet MM, Newman LA, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, Jemal A, Siegel RL. Breast cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(6):438–451. - PubMed
-
- Kos K, Wellenstein M, Vrijland K, Hau CS, De Visser K. PO-386 dissecting the role of regulatory T cells in metastatic breast cancer. In: Tumour Immunology. 2018:A378.373–A379.
-
- Wellenstein MD, Coffelt SB, Duits DEM, van Miltenburg MH, Slagter M, de Rink I, Henneman L, Kas SM, Prekovic S, Hau CS, et al. Loss of p53 triggers WNT-dependent systemic inflammation to drive breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2019;572(7770):538–542. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1450-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

