The Cell-Autonomous Clock of VIP Receptor VPAC2 Cells Regulates Period and Coherence of Circadian Behavior
- PMID: 33234609
- PMCID: PMC7821861
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2015-20.2020
The Cell-Autonomous Clock of VIP Receptor VPAC2 Cells Regulates Period and Coherence of Circadian Behavior
Abstract
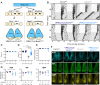
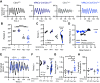
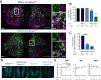
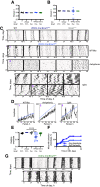
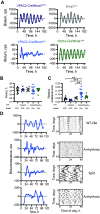
Circadian (approximately daily) rhythms pervade mammalian behavior. They are generated by cell-autonomous, transcriptional/translational feedback loops (TTFLs), active in all tissues. This distributed clock network is coordinated by the principal circadian pacemaker, the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN). Its robust and accurate time-keeping arises from circuit-level interactions that bind its individual cellular clocks into a coherent time-keeper. Cells that express the neuropeptide vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) mediate retinal entrainment of the SCN; and in the absence of VIP, or its cognate receptor VPAC2, circadian behavior is compromised because SCN cells cannot synchronize. The contributions to pace-making of other cell types, including VPAC2-expressing target cells of VIP, are, however, not understood. We therefore used intersectional genetics to manipulate the cell-autonomous TTFLs of VPAC2-expressing cells. Measuring circadian behavioral and SCN rhythmicity in these temporally chimeric male mice thus enabled us to determine the contribution of VPAC2-expressing cells (∼35% of SCN cells) to SCN time-keeping. Lengthening of the intrinsic TTFL period of VPAC2 cells by deletion of the CK1εTau allele concomitantly lengthened the period of circadian behavioral rhythms. It also increased the variability of the circadian period of bioluminescent TTFL rhythms in SCN slices recorded ex vivo Abrogation of circadian competence in VPAC2 cells by deletion of Bmal1 severely disrupted circadian behavioral rhythms and compromised TTFL time-keeping in the corresponding SCN slices. Thus, VPAC2-expressing cells are a distinct, functionally powerful subset of the SCN circuit, contributing to computation of ensemble period and maintenance of circadian robustness. These findings extend our understanding of SCN circuit topology.
Keywords: Bmal1; bioluminescence; casein kinase; circadian rhythm; neuropeptide; suprachiasmatic nucleus.
Copyright © 2021 Hamnett et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential contributions of intra-cellular and inter-cellular mechanisms to the spatial and temporal architecture of the suprachiasmatic nucleus circadian circuitry in wild-type, cryptochrome-null and vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 2-null mutant mice.Eur J Neurosci. 2014 Aug;40(3):2528-40. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12631. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Eur J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24891292 Free PMC article.
-
The mouse VPAC2 receptor confers suprachiasmatic nuclei cellular rhythmicity and responsiveness to vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in vitro.Eur J Neurosci. 2003 Jan;17(2):197-204. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02425.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12542655
-
Aberrant gating of photic input to the suprachiasmatic circadian pacemaker of mice lacking the VPAC2 receptor.J Neurosci. 2004 Apr 7;24(14):3522-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5345-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15071099 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the mammalian circadian clock.J Endocrinol. 2003 Apr;177(1):7-15. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1770007. J Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 12697032 Review.
-
Minireview: The circadian clockwork of the suprachiasmatic nuclei--analysis of a cellular oscillator that drives endocrine rhythms.Endocrinology. 2007 Dec;148(12):5624-34. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0660. Epub 2007 Sep 27. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17901233 Review.
Cited by
-
Circadian Chimeric Mice Reveal an Interplay Between the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus and Local Brain Clocks in the Control of Sleep and Memory.Front Neurosci. 2021 Feb 19;15:639281. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.639281. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33679317 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Mice Affects Neuronal Activity and Glia Cells in the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 27;12(10):2202. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102202. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457515 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo recording of suprachiasmatic nucleus dynamics reveals a dominant role of arginine vasopressin neurons in circadian pacesetting.PLoS Biol. 2023 Aug 29;21(8):e3002281. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002281. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37643163 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Circadian Gas-Responsive Hemeprotein NPAS2 in Physiology and Pathology.Biology (Basel). 2023 Oct 22;12(10):1354. doi: 10.3390/biology12101354. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Timed daily exercise remodels circadian rhythms in mice.Commun Biol. 2021 Jun 18;4(1):761. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02239-2. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34145388 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
