Impaired θ-γ Coupling Indicates Inhibitory Dysfunction and Seizure Risk in a Dravet Syndrome Mouse Model
- PMID: 33234612
- PMCID: PMC7821857
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2132-20.2020
Impaired θ-γ Coupling Indicates Inhibitory Dysfunction and Seizure Risk in a Dravet Syndrome Mouse Model
Abstract
Dravet syndrome (DS) is an epileptic encephalopathy that still lacks biomarkers for epileptogenesis and its treatment. Dysfunction of NaV1.1 sodium channels, which are chiefly expressed in inhibitory interneurons, explains the epileptic phenotype. Understanding the network effects of these cellular deficits may help predict epileptogenesis. Here, we studied θ-γ coupling as a potential marker for altered inhibitory functioning and epileptogenesis in a DS mouse model. We found that cortical θ-γ coupling was reduced in both male and female juvenile DS mice and persisted only if spontaneous seizures occurred. θ-γ Coupling was partly restored by cannabidiol (CBD). Locally disrupting NaV1.1 expression in the hippocampus or cortex yielded early attenuation of θ-γ coupling, which in the hippocampus associated with fast ripples, and which was replicated in a computational model when voltage-gated sodium currents were impaired in basket cells (BCs). Our results indicate attenuated θ-γ coupling as a promising early indicator of inhibitory dysfunction and seizure risk in DS.
Keywords: Dravet syndrome; Nav1.1; epilepsy; interneurons; sodium channels.
Copyright © 2021 the authors.
Figures
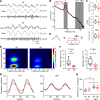
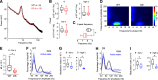
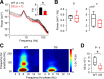
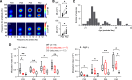
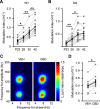
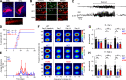
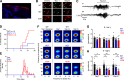
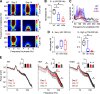
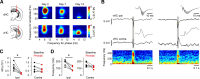
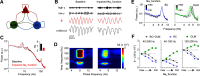
Comment in
-
Symphony Conductors Lose the Baton: Role of Fast-Spiking Interneurons in Orchestrating DS.Epilepsy Curr. 2021 Mar 31;21(3):192-193. doi: 10.1177/15357597211003550. eCollection 2021 May-Jun. Epilepsy Curr. 2021. PMID: 34867101 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Almog Y, Brusel M, Anderson K, Rubinstein M (2019) Early hippocampal hyperexcitability followed by disinhibition in a mouse model of Dravet syndrome. bioRxiv. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/790170.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
