Bleeding and thrombotic risk in pregnant women with Fontan physiology
- PMID: 33234672
- PMCID: PMC10367127
- DOI: 10.1136/heartjnl-2020-317397
Bleeding and thrombotic risk in pregnant women with Fontan physiology
Abstract
Background/objectives: Pregnancy may potentiate the inherent hypercoagulability of the Fontan circulation, thereby amplifying adverse events. This study sought to evaluate thrombosis and bleeding risk in pregnant women with a Fontan.
Methods: We performed a retrospective observational cohort study across 13 international centres and recorded data on thrombotic and bleeding events, antithrombotic therapies and pre-pregnancy thrombotic risk factors.
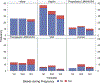
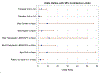
Results: We analysed 84 women with Fontan physiology undergoing 108 pregnancies, average gestation 33±5 weeks. The most common antithrombotic therapy in pregnancy was aspirin (ASA, 47 pregnancies (43.5%)). Heparin (unfractionated (UFH) or low molecular weight (LMWH)) was prescribed in 32 pregnancies (30%) and vitamin K antagonist (VKA) in 10 pregnancies (9%). Three pregnancies were complicated by thrombotic events (2.8%). Thirty-eight pregnancies (35%) were complicated by bleeding, of which 5 (13%) were severe. Most bleeds were obstetric, occurring antepartum (45%) and postpartum (42%). The use of therapeutic heparin (OR 15.6, 95% CI 1.88 to 129, p=0.006), VKA (OR 11.7, 95% CI 1.06 to 130, p=0.032) or any combination of anticoagulation medication (OR 13.0, 95% CI 1.13 to 150, p=0.032) were significantly associated with bleeding events, while ASA (OR 5.41, 95% CI 0.73 to 40.4, p=0.067) and prophylactic heparin were not (OR 4.68, 95% CI 0.488 to 44.9, p=0.096).
Conclusions: Current antithrombotic strategies appear effective at attenuating thrombotic risk in pregnant women with a Fontan. However, this comes with high (>30%) bleeding risk, of which 13% are life threatening. Achieving haemostatic balance is challenging in pregnant women with a Fontan, necessitating individualised risk-adjusted counselling and therapeutic approaches that are monitored during the course of pregnancy.
Keywords: Fontan physiology; pregnancy.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Venous thromboembolism, thrombophilia, antithrombotic therapy, and pregnancy: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition).Chest. 2008 Jun;133(6 Suppl):844S-886S. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-0761. Chest. 2008. PMID: 18574280
-
Bleeding complications and antithrombotic treatment in 264 pregnancies in antiphospholipid syndrome.Lupus. 2018 Sep;27(10):1679-1686. doi: 10.1177/0961203318787032. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Lupus. 2018. PMID: 30016929
-
Use of antithrombotic agents during pregnancy: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy.Chest. 2004 Sep;126(3 Suppl):627S-644S. doi: 10.1378/chest.126.3_suppl.627S. Chest. 2004. PMID: 15383488 Review.
-
[Thrombophilia, preeclampsia and other pregnancy complications].Acta Med Croatica. 2009 Oct;63(4):297-305. Acta Med Croatica. 2009. PMID: 20034330 Review. Croatian.
-
Pregnancy after catheter-directed thrombolysis for acute iliofemoral deep venous thrombosis.Phlebology. 2013 Mar;28 Suppl 1:34-8. doi: 10.1177/0268355513477286. Phlebology. 2013. PMID: 23482532
Cited by
-
Placental Sonomorphologic Appearance and Fetomaternal Outcome in Fontan Circulation.J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 1;13(17):5193. doi: 10.3390/jcm13175193. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39274406 Free PMC article.
-
Cardio-Obstetrics: A Review for the Cardiac Anesthesiologist.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2021 Dec;35(12):3483-3488. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2021.06.012. Epub 2021 Jun 12. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2021. PMID: 34253444 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Navigating women with congenital heart disease during pregnancy: Management strategies and future directions.World J Cardiol. 2025 Jun 26;17(6):106295. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i6.106295. World J Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40575426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary Embolism, Thrombectomy, and Catheter-Directed Lysis in Pregnant Woman With Fontan Palliation.JACC Case Rep. 2025 Jun 25;30(16):103959. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2025.103959. JACC Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40579112 Free PMC article.
-
[Adults with congenital heart disease presenting to the emergency department : Potential pitfalls].Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2022 Mar;117(2):100-111. doi: 10.1007/s00063-020-00752-6. Epub 2020 Oct 25. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2022. PMID: 33103219 Free PMC article. Review. German.
References
-
- Rychik J, Goldberg DJ. Late consequences of the Fontan operation. Circulation 2014;130:1525–8. - PubMed
-
- van den Bosch AE, Roos-Hesselink JW, Van Domburg R, et al. Long-term outcome and quality of life in adult patients after the Fontan operation. Am J Cardiol 2004;93:1141–5. - PubMed
-
- Coon PD, Rychik J, Novello RT, et al. Thrombus formation after the Fontan operation. Ann Thorac Surg 2001;71:1990–4. - PubMed
-
- Balling G, Vogt M, Kaemmerer H, et al. Intracardiac thrombus formation after the Fontan operation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2000;119:745–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
