Kallikrein 13 serves as a priming protease during infection by the human coronavirus HKU1
- PMID: 33234691
- PMCID: PMC7857416
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.aba9902
Kallikrein 13 serves as a priming protease during infection by the human coronavirus HKU1
Abstract
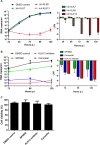
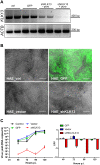
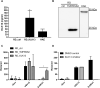
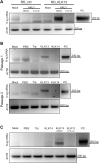
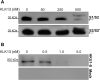
Human coronavirus HKU1 (HCoV-HKU1) is associated with respiratory disease and is prevalent worldwide, but an in vitro model for viral replication is lacking. An interaction between the coronaviral spike (S) protein and its receptor is the primary determinant of tissue and host specificity; however, viral entry is a complex process requiring the concerted action of multiple cellular elements. Here, we found that the protease kallikrein 13 (KLK13) was required for the infection of human respiratory epithelial cells and was sufficient to mediate the entry of HCoV-HKU1 into nonpermissive RD cells. We also demonstrated the cleavage of the HCoV-HKU1 S protein by KLK13 in the S1/S2 region, suggesting that KLK13 is the priming enzyme for this virus. Together, these data suggest that protease distribution and specificity determine the tissue and cell specificity of the virus and may also regulate interspecies transmission.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of the Receptor-Binding Domain of the Spike Glycoprotein of Human Betacoronavirus HKU1.J Virol. 2015 Sep;89(17):8816-27. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03737-14. Epub 2015 Jun 17. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26085157 Free PMC article.
-
Human Coronavirus HKU1 Spike Protein Uses O-Acetylated Sialic Acid as an Attachment Receptor Determinant and Employs Hemagglutinin-Esterase Protein as a Receptor-Destroying Enzyme.J Virol. 2015 Jul;89(14):7202-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00854-15. Epub 2015 Apr 29. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25926653 Free PMC article.
-
The host protease KLK5 primes and activates spike proteins to promote human betacoronavirus replication and lung inflammation.Sci Signal. 2024 Aug 20;17(850):eadn3785. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.adn3785. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Sci Signal. 2024. PMID: 39163389
-
Properties of Coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2.Malays J Pathol. 2020 Apr;42(1):3-11. Malays J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32342926 Review.
-
Gene of the month: the 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2 novel coronavirus spike protein.J Clin Pathol. 2020 Jul;73(7):366-369. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206658. Epub 2020 May 6. J Clin Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32376714 Review.
Cited by
-
Kallikreins emerge as new regulators of viral infections.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Nov;78(21-22):6735-6744. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03922-7. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34459952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The plasma proteome differentiates the multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) from children with SARS-CoV-2 negative sepsis.Mol Med. 2024 Apr 17;30(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00806-x. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38632526 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolysis and Deficiency of α1-Proteinase Inhibitor in SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Biochem Mosc Suppl B Biomed Chem. 2022;16(4):271-291. doi: 10.1134/S1990750822040035. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Biochem Mosc Suppl B Biomed Chem. 2022. PMID: 36407837 Free PMC article.
-
Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal (Ashwagandha) for the possible therapeutics and clinical management of SARS-CoV-2 infection: Plant-based drug discovery and targeted therapy.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Aug 15;12:933824. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.933824. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36046742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host Cell Proteases Involved in Human Respiratory Viral Infections and Their Inhibitors: A Review.Viruses. 2024 Jun 19;16(6):984. doi: 10.3390/v16060984. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38932275 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- B. N. Fields, D. M. Knipe, P. M. Howley, Fields Virology (Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, ed. 6, 2013).
-
- Peiris J. S., Yuen K. Y., Osterhaus A. D. M. E., Stöhr K., The severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 349, 2431–2441 (2003). - PubMed
-
- de Groot R. J., Baker S. C., Baric R. S., Brown C. S., Drosten C., Enjuanes L., Fouchier R. A. M., Galiano M., Gorbalenya A. E., Memish Z. A., Perlman S., Poon L. L. M., Snijder E. J., Stephens G. M., Woo P. C. Y., Zaki A. M., Zambon M., Ziebuhr J., Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV): Announcement of the Coronavirus Study Group. J. Virol. 87, 7790–7792 (2013). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zaki A. M., van Boheemen S., Bestebroer T. M., Osterhaus A. D. M. E., Fouchier R. A., Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 367, 1814–1820 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

