Bridging and downstaging role of trans-arterial radio-embolization for expected small remnant volume before liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 33234744
- PMCID: PMC7691198
- DOI: 10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.4.421
Bridging and downstaging role of trans-arterial radio-embolization for expected small remnant volume before liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Bridging and downstaging role of trans-arterial radio-embolization for expected small remnant volume before liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma.Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2021 Nov 30;25(4):575. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.4.575. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2021. PMID: 34845135 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
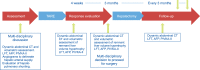
Backgrounds/aims: To evaluate our initial experience of bridging role of trans-arterial radio-embolization (TARE) before major hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in risky patients with small expected remnant liver volume (ERLV).
Methods: We reviewed the data of patients with HCC who underwent major hepatectomy after TARE during the period between March and December 2017. Patients included had uni-lobar large HCC (>5 cm) requiring major hepatectomy with small ERLV.
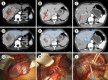
Results: Five patients were included in our study. All patients were Child Pugh class A. A single session of TARE was applied in all patients. None developed any adverse events related to irradiation. The mean tumor size at baseline was 8.4 cm and 6.1 cm after TARE (p=0.077). The mean % of tumor shrinkage was 24.5%. ERLV improved from 354.6 ml at baseline to 500.8 ml after TARE (p=0.012). ERLV percentage improved from 27.2% at baseline to 38.1% after TARE (p=0.004). The mean % of ERLV was 39.5%. The mean interval time between TARE and resection was 99.6 days. Four patients (80%) underwent right hemi-hepatectomy and one patient (20%) underwent extended right hemi-hepatectomy. The mean operation time was 151 minutes, and mean blood loss was 56 ml. The mean hospital stay was 13.8 days, and one patient (20%) developed postoperative morbidity. After a mean follow-up of 15 months, all patients were alive with no recurrence.
Conclusions: Yttrium-90 TARE can play a bridging role before major hepatectomy for borderline resectable HCC in risky patients with small ERLV.
Keywords: Major liver resection; Small remnant liver volume; Trans-arterial radio-embolization.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Outcomes of Surgical Resection after Radioembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2018 Nov;29(11):1502-1510.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2018.06.027. Epub 2018 Sep 27. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2018. PMID: 30268638
-
Feasibility and safety of liver transplantation or resection after transarterial radioembolization with Yttrium-90 for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.HPB (Oxford). 2019 Nov;21(11):1497-1504. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2019.03.360. Epub 2019 Apr 17. HPB (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 31005494
-
Ablative-Transarterial Radioembolization resulting in complete histopathological response of hepatocellular carcinoma in the resected liver specimen after salvage hepatectomy.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2022 Jan;90:106679. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2021.106679. Epub 2021 Dec 28. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 34972009 Free PMC article.
-
Selecting the Appropriate Downstaging and Bridging Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What Is the Role of Transarterial Radioembolization? A Pooled Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 2;15(7):2122. doi: 10.3390/cancers15072122. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transarterial radioembolization using yttrium-90 microspheres in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a review on clinical utility and developments.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2014 Nov 3;1:163-82. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S50472. eCollection 2014. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2014. PMID: 27508185 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biochemical Safety of Ablative Yttrium-90 Radioembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma as a Function of Percent Liver Treated.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2021 Jul 30;8:861-870. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S319215. eCollection 2021. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2021. PMID: 34368021 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Unilateral 90Y-radioembolization on Functional Changes in the Contralateral Hepatic Lobe: The Prospective, Open-label RadioEmbolization, Volumetry, and Liver FuncTion Measurements (REVoluTion) Study.Ann Surg Open. 2021 Sep 2;2(3):e095. doi: 10.1097/AS9.0000000000000095. eCollection 2021 Sep. Ann Surg Open. 2021. PMID: 37635822 Free PMC article.
-
KSNM60 in Non-thyroidal Radionuclide Therapy: Leaping into the Future.Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 Oct;55(5):203-209. doi: 10.1007/s13139-021-00703-9. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34721713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma beyond the Milan Criteria: A Specific Role for Living Donor Liver Transplantation after Neoadjuvant Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 25;16(5):920. doi: 10.3390/cancers16050920. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473282 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial Radioembolization for Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Oncologist. 2024 Feb 2;29(2):117-122. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad327. Oncologist. 2024. PMID: 38128565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Makuuchi M, Thai BL, Takayasu K, Takayama T, Kosuge T, Gunvén P, et al. Preoperative portal embolization to increase safety of major hepatectomy for hilar bile duct carcinoma: a preliminary report. Surgery. 1990;107:521–527. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
