Topical use of Jiawei Simiao Yongan Gao to prevent radiodermatitis in patients with head and neck cancer: A retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 33235092
- PMCID: PMC7710264
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023318
Topical use of Jiawei Simiao Yongan Gao to prevent radiodermatitis in patients with head and neck cancer: A retrospective cohort study
Abstract
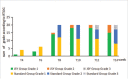
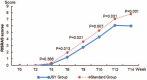
Radiodermatitis is a common side effect of radiotherapy, but currently there is no standard treatment for its prevention. This study aimed to observe the effect of topical application of a paste based on traditional Chinese medicine, Jiawei Simiao Yongan Gao, on radiodermatitis caused by radiotherapy for patients with head and neck cancer.This was a retrospective cohort study of 40 patients with head and neck cancer evaluated during their radiotherapy. Of these, 20 patients were treated with Jiawei Simiao Yongan Gao on the irradiated skin from the beginning of radiotherapy (JSY group). The other 20 patients were given standard nursing (standard group). Acute skin reactions were classified according to the radiation-induced skin reaction assessment scale (RISRAS) and American radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) acute toxicity grading criteria every 2 weeks, and adverse effects were recorded until the end of the radiotherapy.The two groups showed differences in severity of radiodermatitis. At 0 to 30 Gy, the skin reactions were similar in the two groups, while above 40 Gy the skin reactions were significantly lower grade in the JSY group (P < .05). At 0 to 20 Gy, there was no statistical significance (P > .05); but above 30 Gy they were lower in the JSY group (P < .05).Jiawei Simiao Yongan Gao effectively alleviated acute radiodermatitis caused by radiotherapy of head and neck cancer patients compared with standard nursing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiotherapy related skin toxicity (RAREST-01): Mepitel® film versus standard care in patients with locally advanced head-and-neck cancer.BMC Cancer. 2018 Feb 17;18(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4119-x. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29454311 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Topical application of a sandal wood oil and turmeric based cream prevents radiodermatitis in head and neck cancer patients undergoing external beam radiotherapy: a pilot study.Br J Radiol. 2014 Jun;87(1038):20130490. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20130490. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Br J Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24694358 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Consensus guidelines for the management of radiation dermatitis and coexisting acne-like rash in patients receiving radiotherapy plus EGFR inhibitors for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Ann Oncol. 2008 Jan;19(1):142-9. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdm400. Epub 2007 Sep 4. Ann Oncol. 2008. PMID: 17785763
-
A monocentric, open-label randomized standard-of-care controlled study of XONRID®, a medical device for the prevention and treatment of radiation-induced dermatitis in breast and head and neck cancer patients.Radiat Oncol. 2020 Aug 13;15(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-01633-0. Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32791985 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Team Health Education on Radiodermatitis in Patients with Head and Neck Tumor Radiotherapy Under the Joint Committee International Standards.Semin Oncol Nurs. 2021 Jun;37(3):151148. doi: 10.1016/j.soncn.2021.151148. Epub 2021 May 16. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2021. PMID: 34011460 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevention of Radiodermatitis With Topical Chinese Herbal Medicine: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 22;13:819733. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.819733. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35814240 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and analysis of Simiao Yong'an Decoction fermentation by Bacillus subtilis on the diversity of intestinal microbiota in Sprague-Dawley rats.Vet World. 2024 Mar;17(3):712-719. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.712-719. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Vet World. 2024. PMID: 38680148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Häfner MF, Fetzner L, Hassel JC, et al. Prophylaxis of acute radiation dermatitis with an innovative FDA-approved two-step skin care system in a patient with head and neck cancer undergoing a platin-based radiochemotherapy: a case report and review of the literature. Dermatology 2013;227:171–4. - PubMed
-
- Cabezón-Gutiérrez L, Khosravi-Shahi P, Escobar-Álvarez Y. Management of dermatitis in patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck receiving cetuximab and radiotherapy. Oral Oncol 2012;48:293–7. - PubMed
-
- Iacovelli NA, Galaverni M, Cavallo A, et al. Prevention and treatment of radiation-induced acute dermatitis in head and neck cancer patients: a systematic review. Future Oncol 2018;14:291–305. - PubMed
-
- Hegedus F, Mathew LM, Schwartz RA. Radiation dermatitis: an overview. Int J Dermatol 2017;56:909–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

