Up-Regulation of miR-26a-5p Inhibits E2F7 to Regulate the Progression of Renal Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 33235501
- PMCID: PMC7680095
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S271710
Up-Regulation of miR-26a-5p Inhibits E2F7 to Regulate the Progression of Renal Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
Background: Metastasis is the main cause of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) tumor death, and effective inhibition of RCC metastasis is an essential means to meliorate the prognosis of RCC patients. MicroRNAs (miRs) have been proved to be stable and important biomarkers for several malignancies. This study is therefore set out to explore the metastasis-related miR and its mechanism in RCC.
Methods: The expression of miR- 26a -5p in RCC was analyzed using the expression profile in the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). MiR-26a-5p and E2F transcription factor 7 (E2F7) in RCC patients were detected by qRT-PCR. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) was adopted to assess cell proliferation, Transwell was utilized to evaluate migration and invasion, and flow cytometry (FC) was used to determine apoptosis. Mouse cell-derived and patient-derived xenotransplantation models were established to evaluate the effect of miR-26a-5p on tumor growth and metastasis in vivo. The molecular mechanism of miR-26a-5p was analyzed by dual-luciferase reporter (DLR) gene analysis, qRT-PCR, and Western blot (WB) both in vivo and in vitro.
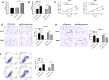
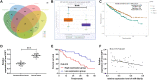
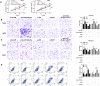
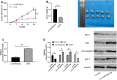
Results: MiR-26a-5p was reduced in renal carcinoma cells and may serve as a biomarker for renal cancer metastasis and prognosis. MiR-26a-5p up-regulation inhibited migration and invasion in renal cell lines and tumor metastasis in vivo. Bioinformatics target prediction and RNA-seq results showed that E2F7 was among the targets of miR-26a-5p and was significantly inhibited by miR-26a-5p in vivo and in vitro.
Conclusion: MiR-26a-5p presents low expression in RCC and promotes RCC cell apoptosis and prevents cells from proliferating and invading by targeting E2F7, which is a promising therapeutic target for RCC.
Keywords: E2F7; invasion; miR-26a-5p; proliferation; renal cell carcinoma.
© 2020 Cheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

