Comprehensive Survey of Plagiarism in Iran
- PMID: 33235554
- PMCID: PMC7674871
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.36.7.3456
Comprehensive Survey of Plagiarism in Iran
Abstract
Background and objective: We conducted this study to assess the prevalence of plagiarism and to shed light on some dark aspects of this issue. The main objectives included to find out the etiology, prevalence, and detection of various forms plagiarism.
Methods: In this Cross-sectional study we used a questionnaire, face-to-face interview, analyzing the present notifications and codes, websites, and literature review. The current study was conducted throughout Iran from 2017-2018. Those associated with scientific journalism, academic staffs, and authors were interviewed or asked to fill out a prepared questionnaire.
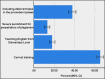
Results: Nine hundred seventy nine questionnaires were circulated. Out of this 706 (72.1%) were completed and returned. Those with a master degree were most cooperative in filling out the questionnaires (36.4%); followed by Assistant Professors (29.6%). About 74.1% of respondents, had not participated in any educational workshops on plagiarism (P<0.001) while 10.8% had not heard anything about plagiarism (P<0.001). As regards correct reply as for definition and detecting plagiarism; 91.1%, 40.8%, 48.4% and 57.9% could reply correctly (P<0.001). Forty-one-point one percent of the participants believed that reprimand would be the best punishment. The percentage of plagiarism as per people associated in journal administration, was 22.9%; based on experts' opinions, it was 30.0%; and based on analysis of some journals published in Iran, it was 25.5%.
Conclusion: We found a noticeable prevalence of plagiarism in Iran. Many factors are involved in this misconduct; most important being the need for academic staff and students to publish e more papers regardless of their quality to meet some of the academic requirements. Considering the high rank of Iran in terms of scientific growth worldwide, it is expected from the regulatory authorities to monitor all aspects of scientific misconducts in medical journalism.
Keywords: Iran; Plagiarism; Publication ethics; Scientific Misconduct.
Copyright: © Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combating Scientific Misconduct: The Role of Focused Workshops in Changing Attitudes Towards Plagiarism.Cureus. 2018 May 28;10(5):e2698. doi: 10.7759/cureus.2698. Cureus. 2018. PMID: 30062072 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring scientific misconduct in Morocco based on an analysis of plagiarism perception in a cohort of 1,220 researchers and students.Account Res. 2024 Dec;31(2):138-157. doi: 10.1080/08989621.2022.2110866. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Account Res. 2024. PMID: 35938392
-
Plagiarism, Fake Peer-Review, and Duplication: Predominant Reasons Underlying Retractions of Iran-Affiliated Scientific Papers.Sci Eng Ethics. 2020 Dec;26(6):3455-3463. doi: 10.1007/s11948-020-00274-6. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Sci Eng Ethics. 2020. PMID: 33146787
-
Plagiarism in scientific research and publications and how to prevent it.Mater Sociomed. 2014 Apr;26(2):141-6. doi: 10.5455/msm.2014.26.141-146. Epub 2014 Apr 11. Mater Sociomed. 2014. PMID: 24944543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iranian academia: evolution after revolution and plagiarism as a disorder.Sci Eng Ethics. 2011 Jun;17(2):213-6. doi: 10.1007/s11948-010-9206-6. Epub 2010 May 29. Sci Eng Ethics. 2011. PMID: 20512425 Review.
Cited by
-
Plagiarism detection and prevention: a primer for researchers.Reumatologia. 2021;59(3):132-137. doi: 10.5114/reum.2021.105974. Epub 2021 May 13. Reumatologia. 2021. PMID: 34538939 Free PMC article.
-
Plagiarism in Non-Anglophone Countries: a Cross-sectional Survey of Researchers and Journal Editors.J Korean Med Sci. 2021 Oct 11;36(39):e247. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e247. J Korean Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34636502 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing research misconduct in Iran: a perspective from Iranian medical faculty members.BMC Med Ethics. 2021 Jun 21;22(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12910-021-00642-2. BMC Med Ethics. 2021. PMID: 34154574 Free PMC article.
-
Plagiarism: A Bird's Eye View.J Korean Med Sci. 2023 Nov 20;38(45):e373. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e373. J Korean Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37987104 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Merriam-Webster. Definition of plagiarize. 2020. [Accessed 23 March 2020]. Available from: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/plagiarize .
-
- Science AAftAo. This week's section. Science. 2014;346(6215):1272–1274.
-
- Ghajarzadeh M, Norouzi-Javidan A, Hassanpour K, Aramesh K, Emami-Razavi SH. Attitude toward plagiarism among Iranian medical faculty members. Acta Med Iran. 2012;50(11):778–781. - PubMed
-
- Gharedaghi MH, Nourijelyani K, Sadaghiani MS, Yousefzadeh-Fard Y, Gharedaghi A, Javadian P, et al. Knowledge of medical students of Tehran University of Medical Sciences regarding plagiarism. Acta Med Iran. 2013;51(6):418. - PubMed
-
- Ghazinoory S, Ghazinoori S, Azadegan-Mehr M. Iranian academia:evolution after revolution and plagiarism as a disorder. Sci Eng Ethics. 2011;17(2):213–216. doi:10.1007/s11948-010-9206-6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials