Anti-inflammatory activity of Radix Angelicae biseratae in the treatment of osteoarthritis determined by systematic pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- PMID: 33235614
- PMCID: PMC7678626
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9437
Anti-inflammatory activity of Radix Angelicae biseratae in the treatment of osteoarthritis determined by systematic pharmacology and in vitro experiments
Abstract
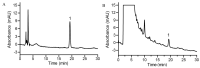
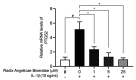
Radix Angelicae biseratae is a widely used Chinese traditional herbal medicine for osteoarthritis (OA). Its therapeutic efficacy has been confirmed in clinical practice. However, its mechanisms of action in treating OA have remained elusive. The purpose of the present study was to identify active components with good oral bioavailability and drug-like properties from Radix Angelicae biseratae through systematic pharmacology and in vitro experiments to determine targets of Radix Angelicae biseratae in the treatment of OA. The functional components of Radix Angelicae biseratae were screened from the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology database based on oral bioavailability and drug-like properties. Subsequently, the databases STITCH, Open Targets Platform and DrugBank were searched and microarray analysis was performed to screen the active components of Radix Angelicae biseratae to treat OA and predict its potential target proteins. The interaction network and protein interaction network were then generated and examined, molecular docking between active components and targets was performed and the enrichment of potential target proteins was analyzed. Finally, reverse transcription-quantitative (RT-q)PCR and western blot analyses were used to verify the therapeutic effect of Radix Angelicae biseratae extract on the expression of OA-associated target proteins. The results provided eight active components in Radix Angelicae biseratae, which were firmly linked to 20 targets of OA. In combination with molecular docking and the analysis of the interaction network between components and targets, it was suggested that sitosterol was a major active component of Radix Angelicae biseratae in the treatment of OA. Protein interaction network analysis suggested that prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS2), nitric oxide synthase 3 and cytochrome P450 2B6 may be critical targets for Radix Angelicae biseratae in the treatment of OA. In addition, RT-qPCR and western blot analyses suggested that Radix Angelicae biseratae extract inhibited the mRNA and protein expression of PTGS2 in degenerative articular cartilage cells in vitro, whilst other targets remain to be verified. Functional enrichment analysis indicated that Radix Angelicae biseratae confers pharmacological efficacy towards OA through exerting anti-inflammatory effects and immune regulation.
Keywords: Radix Angelicae biseratae; anti- inflammation; molecular mechanism; osteoarthritis; systematic pharmacology; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright: © Chen et al.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
