Role of TGF-β1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the pathogenesis of tympanosclerosis
- PMID: 33235615
- PMCID: PMC7678609
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9438
Role of TGF-β1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the pathogenesis of tympanosclerosis
Abstract
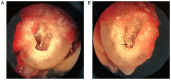
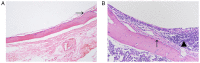
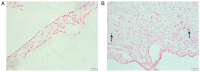
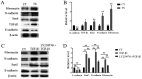
The present study aimed to explore the role of TGF-β1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in the pathogenesis of tympanosclerosis. Sprague Dawley rats were injected with inactivated Streptococcus pneumoniae suspension to establish a rat model of tympanosclerosis. The rats were sacrificed 8 weeks after the model was established. H&E and von Kossa staining was used to observe the morphological changes of middle ear mucosa. Western blotting was used to detect the expression of TGF-β1 and EMT-associated proteins in the mucosa samples. Middle ear mucosal epithelial cells of rats were collected to establish a primary culture. The cultured cells were stimulated with TGF-β1 and the expression of EMT-associated proteins was detected by western blotting and immunofluorescence. In addition, the cells were treated with TGF-β receptor type I/II inhibitor and the expression level of EMT-associated proteins was detected by western blotting. Sclerotic lesions appeared on 72.4% of tympanic membranes, and marked inflammation, inflammatory cell infiltration and fibrosis were found in the middle ear mucosa of rat models of tympanosclerosis. In middle ear mucosa of rats with tympanosclerosis, the expression of mesenchymal cell markers increased and that of epithelial cell markers decreased compared with the control group. TGF-β1 stimulated the activation of the EMT pathway in middle ear mucosal epithelial cells, resulting in an increased expression of fibronectin and N-cadherin. In addition, a decreased expression level of EMT-associated proteins was observed when TGF-β1 was inhibited. In conclusion, the present study indicated that TGF-β1-mediated EMT may play an important role in the pathogenesis of tympanosclerosis.
Keywords: N-cadherin; TGF-β1; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; fibronectin; tympanosclerosis.
Copyright: © Qiu et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TGF-beta1 induces human alveolar epithelial to mesenchymal cell transition (EMT).Respir Res. 2005 Jun 9;6(1):56. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-6-56. Respir Res. 2005. PMID: 15946381 Free PMC article.
-
Expressions of TGF-β1 and MMP-9 in a guinea pig model of tympanosclerosis: possible role in the pathogenesis of this disorder.Laryngoscope. 2012 Sep;122(9):2037-42. doi: 10.1002/lary.23415. Epub 2012 Jul 9. Laryngoscope. 2012. PMID: 22777961
-
TGF-β1 Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Chronic Sinusitis with Nasal Polyps through MicroRNA-21.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2019;179(4):304-319. doi: 10.1159/000497829. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30982052
-
Qinggan Huoxue Recipe suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in alcoholic liver fibrosis through TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 May 21;22(19):4695-706. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i19.4695. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27217701 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of TGF-β1 and EGFR in Cleft Affected Lip Mucosa.Acta Med Litu. 2021;28(1):86-96. doi: 10.15388/Amed.2021.28.1.14. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Acta Med Litu. 2021. PMID: 34393631 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lymphocytic Airway Inflammation in Lung Allografts.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 12;13:908693. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.908693. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35911676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of TGF-β signaling enables long-term proliferation of mouse primary epithelial stem/progenitor cells of the tympanic membrane and the middle ear mucosa.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 20;13(1):4532. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31246-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36941290 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of Gut Microbiota in Patients With Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jul 4;13:913718. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.913718. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35865926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qiu JJ, Wang JX, Sun Y. Advances in research on etiology of tympanosclerosis and related factors. Chin J Otol. 2020;18:792–796.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
