Short- and long-term treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or calcium channel blockers for the prevention of diabetic nephropathy progression: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 33235623
- PMCID: PMC7678606
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9446
Short- and long-term treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or calcium channel blockers for the prevention of diabetic nephropathy progression: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Treatments with angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or calcium channel blockers (CCBs) may delay the development of albuminuria in patients with early diabetic nephropathy. However, evidence in the literature has not been consistent. The present meta-analysis aimed to compare the short- and long-term therapeutic effects of ACE inhibitors and CCBs (when used separately) for preventing the progression of nephropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus. A comprehensive search of various databases was performed from inception until March 2015 for studies in the Chinese and English languages. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing the efficacy of ACE inhibitors with that of CCBs in patients with early diabetic nephropathy were considered. A total of 12 RCTs were included with a total of 947 patients. ACE inhibitors were indicated to be more effective in reducing the albumin excretion rate than CCBs after short-term treatments (<6 months) [mean difference (MD), 32.35; 95% confidence interval (CI), 31.62-33.07; P<0.00001]. There was no difference in serum creatinine values after treatment with either drug (MD, 8.7; 95% CI, -21.5-38.91; P=0.57). Data from six studies were used to compare long-term treatment effects (≥1 year). In terms of progression to normoalbuminuria, a marginal difference was obtained between the two drugs with better outcomes with ACE inhibitors [odds ratio (OR), 0.70; 95% CI, 0.49-1.00; P=0.05]. There was no statistically significant difference between ACE inhibitors and CCBs regarding the progression from microalbuminuria to macroalbuminuria (OR, 1.78; 95% CI, 0.82-3.87; P=0.15). In conclusion, the present study indicated that the antiproteinuric efficacy of CCBs may be less than that of ACE inhibitors after short-term treatment in patients with DN. However, both types of drugs are equally effective in reducing the progression of microalbuminuria to macroalbuminuria in the long term.
Keywords: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; calcium channel blockers; early diabetic nephropathy; meta-analysis.
Copyright: © Liang et al.
Figures

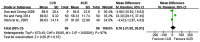
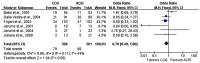

Similar articles
-
Pharmacologic management of diabetic nephropathy.Clin Ther. 2002 Nov;24(11):1741-56; discussion 1719. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(02)80076-5. Clin Ther. 2002. PMID: 12501871 Review.
-
Comparing the Efficacy of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors with Calcium Channel Blockers on the Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy: A Meta-Analysis.Iran J Public Health. 2019 Feb;48(2):189-197. Iran J Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31205872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic approaches to slowing the progression of diabetic nephropathy - is less best?Drugs Context. 2013 Mar 27;2013:212249. doi: 10.7573/dic.212249. eCollection 2013 Mar 27. Drugs Context. 2013. PMID: 24432038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of adding tripterygium glycosides to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers on albuminuria in patients with diabetic nephropathy.Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2020 Feb 10;6(1):18-26. doi: 10.1016/j.cdtm.2019.12.008. eCollection 2020 Mar. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32226931 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective study of the effects of angiotensin receptor blockers and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in diabetic nephropathy.Indian J Pharmacol. 2015 Mar-Apr;47(2):148-52. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.153420. Indian J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25878372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: Results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Lancet. 2000;355:253–259. Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators. - PubMed
-
- Hu R, Yang Z. Study on effect of the combined treatment of enalapril and amlodipine in elderly diabetic patients with hypertension. Diabetes New World. 2014;24:6–7. (In Chinese)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
