Classification of COVID-19 chest X-rays with deep learning: new models or fine tuning?
- PMID: 33235710
- PMCID: PMC7680558
- DOI: 10.1007/s13755-020-00135-3
Classification of COVID-19 chest X-rays with deep learning: new models or fine tuning?
Abstract
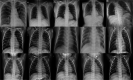
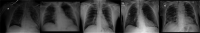
Background and objectives: Chest X-ray data have been found to be very promising for assessing COVID-19 patients, especially for resolving emergency-department and urgent-care-center overcapacity. Deep-learning (DL) methods in artificial intelligence (AI) play a dominant role as high-performance classifiers in the detection of the disease using chest X-rays. Given many new DL models have been being developed for this purpose, the objective of this study is to investigate the fine tuning of pretrained convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for the classification of COVID-19 using chest X-rays. If fine-tuned pre-trained CNNs can provide equivalent or better classification results than other more sophisticated CNNs, then the deployment of AI-based tools for detecting COVID-19 using chest X-ray data can be more rapid and cost-effective.
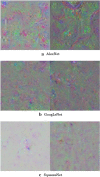
Methods: Three pretrained CNNs, which are AlexNet, GoogleNet, and SqueezeNet, were selected and fine-tuned without data augmentation to carry out 2-class and 3-class classification tasks using 3 public chest X-ray databases.
Results: In comparison with other recently developed DL models, the 3 pretrained CNNs achieved very high classification results in terms of accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, score, and area under the receiver-operating-characteristic curve.
Conclusion: AlexNet, GoogleNet, and SqueezeNet require the least training time among pretrained DL models, but with suitable selection of training parameters, excellent classification results can be achieved without data augmentation by these networks. The findings contribute to the urgent need for harnessing the pandemic by facilitating the deployment of AI tools that are fully automated and readily available in the public domain for rapid implementation.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; COVID-19; Chest X-rays; Classification; Deep learning.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestThe author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
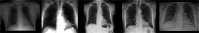

Similar articles
-
Deep Learning Algorithm for COVID-19 Classification Using Chest X-Ray Images.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Nov 9;2021:9269173. doi: 10.1155/2021/9269173. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. PMID: 34795794 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study for glioma classification using deep convolutional neural networks.Math Biosci Eng. 2021 Jan 29;18(2):1550-1572. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2021080. Math Biosci Eng. 2021. PMID: 33757198
-
Classification of the ICU Admission for COVID-19 Patients with Transfer Learning Models Using Chest X-Ray Images.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 26;15(7):845. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15070845. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218195 Free PMC article.
-
Development and integration of VGG and dense transfer-learning systems supported with diverse lung images for discovery of the Coronavirus identity.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;32:101004. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.101004. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35822170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Data-driven classification and explainable-AI in the field of lung imaging.Front Big Data. 2024 Sep 19;7:1393758. doi: 10.3389/fdata.2024.1393758. eCollection 2024. Front Big Data. 2024. PMID: 39364222 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Multi-Task Model for Pulmonary Nodule Segmentation and Classification.J Imaging. 2024 Sep 20;10(9):234. doi: 10.3390/jimaging10090234. J Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39330454 Free PMC article.
-
Classifying COVID-19 Patients From Chest X-ray Images Using Hybrid Machine Learning Techniques: Development and Evaluation.JMIR Form Res. 2023 Feb 28;7:e42324. doi: 10.2196/42324. JMIR Form Res. 2023. PMID: 36780315 Free PMC article.
-
A fine-tuned YOLOv5 deep learning approach for real-time house number detection.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2023 Jul 3;9:e1453. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1453. eCollection 2023. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2023. PMID: 37547390 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer Learning for the Detection and Diagnosis of Types of Pneumonia including Pneumonia Induced by COVID-19 from Chest X-ray Images.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Aug 16;11(8):1480. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11081480. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34441414 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of COVID-19 in X-ray images by classification of bag of visual words using neural networks.Biomed Signal Process Control. 2021 Jul;68:102750. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102750. Epub 2021 May 14. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2021. PMID: 34007303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Imaging the Coronavirus Disease COVID-19. https://healthcare-in-europe.com/en/news/imaging-the-coronavirus-disease....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

