P2X3 receptor expression in dorsal horn of spinal cord and pain threshold after estrogen therapy for prevention therapy in neuropathic pain
- PMID: 33235714
- PMCID: PMC7670236
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2020.11.013
P2X3 receptor expression in dorsal horn of spinal cord and pain threshold after estrogen therapy for prevention therapy in neuropathic pain
Abstract
Introduction: Neuropathic pain may arise from conditions that affecting the central or peripheral nervous system. This study was held to determine the difference P2X3 receptor expression in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and pain threshold after estrogen therapy in neuropathic pain.
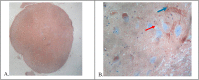
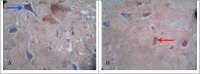
Methods: This study design was an experimental research laboratory. The 24 mice samples divided into negative control group, positive control, and treatment groups. The treatment groups were given subcutaneous injections of estrogen 0.4 ml and also examined for the onset of thermal hyperalgesia in every rat. On day 15, an autopsy was performed on rats, and the spine was taken. The spinal cord was stained by hematoxylin-eosin, and the expression of P2X3 receptors was investigated. P2X3 receptor expression was examined in the dorsal horn on each sample.
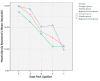
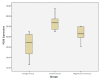
Results: From 24 subjects of the study revealed an increase in the onset of thermal hyperalgesia on the estrogen group compared with the placebo group, a higher start. This study also obtained a decrease in the expression of P2X3 on the therapy group compared to the positive control group with significant differences. Statistical test results revealed the appearance of the P2X3 estrogen group had a substantial difference with the placebo group (p = 0.000) and the mean of the negative control group (p = 0.030). The placebo group had a significant difference from the negative control group (p = 0.035).
Conclusion: Estrogen could decrease the expression of P2X3 receptors and prolonged the onset of thermal hyperalgesia. So, both of these explained that estrogen has a role in preventing the occurrence of neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve lesions.
Keywords: Estrogen; Neuropathic pain; P2X3 receptor; Prevention therapy; Thermal hypealgesia.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pregabalin alters nociceptive behavior and expression level of P2X3 receptor in the spinal dorsal horn in a rat model induced by chronic compression of the dorsal root ganglion.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2013 Dec;296(12):1907-12. doi: 10.1002/ar.22816. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2013. PMID: 24136739
-
Effects of 1,8-cineole on neuropathic pain mediated by P2X2 receptor in the spinal cord dorsal horn.Sci Rep. 2019 May 27;9(1):7909. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44282-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31133659 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of intermedin on dorsal root ganglia in the transmission of neuropathic pain in chronic constriction injury rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015 Jul;42(7):780-7. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12416. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25951228
-
Electroacupuncture and A-317491 depress the transmission of pain on primary afferent mediated by the P2X3 receptor in rats with chronic neuropathic pain states.J Neurosci Res. 2014 Dec;92(12):1703-13. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23451. Epub 2014 Jul 17. J Neurosci Res. 2014. PMID: 25041872
-
Effects of nanoparticle-encapsulated curcumin on HIV-gp120-associated neuropathic pain induced by the P2X3 receptor in dorsal root ganglia.Brain Res Bull. 2017 Oct;135:53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.09.011. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Brain Res Bull. 2017. PMID: 28962965
Cited by
-
Estrogen modulation of the pronociceptive effects of serotonin on female rat trigeminal sensory neurons is timing dependent and dosage dependent and requires estrogen receptor alpha.Pain. 2022 Aug 1;163(8):e899-e916. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002604. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Pain. 2022. PMID: 35121697 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen-dependent regulation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) and P2X purinoceptor 3 (P2X3): Implication in burning mouth syndrome.J Dent Sci. 2022 Jan;17(1):8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2021.06.007. Epub 2021 Jul 1. J Dent Sci. 2022. PMID: 35028015 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marcus D.A., Core D.K., Deodhar A., Payne R. Clinical Publising Oxford; Oxon UK: 2009. An Atlas of Investigation and Management Chronic Pain; pp. 1–14.
-
- Sinanović O. Neuropathic pain. Acta Clin. Croat. 2010;49(Suppl) No. 2.
-
- Alles Sascha RA., Smith Peter A. Etiology and Pharmacology of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018;70(2):315–347. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources