Counter-regulatory responses to Telfairia occidentalis-induced hypoglycaemia
- PMID: 33235989
- PMCID: PMC7670218
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metop.2020.100065
Counter-regulatory responses to Telfairia occidentalis-induced hypoglycaemia
Abstract
Background: Telfairia occidentalis (TO) has many biological activities including blood glucose regulation. Thus, it is being used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. TO has been shown to cause insulin-mediated hypoglycaemia, which leads to post-hypoglycaemic hyperglycaemia. However, the mechanism involved in the post-hypoglycaemic hyperglycaemia is still poorly understood.
Objective: This research was designed to determine the response of glucoregulatory hormones and enzymes to TO treatment.
Methods: Thirty-five male Wistar rats were divided into seven oral treatment groups (n = 5/group), which received either of 100 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg TO for 7-, 10- or 14 days.
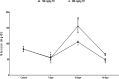
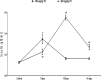
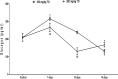
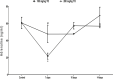
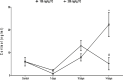
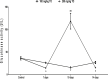
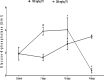
Results: The 7-day treatment with TO significantly increased the levels of insulin, glucagon, and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) activity but decreased the levels of glucose, adrenaline, and glucokinase (GCK) activity. The 10-day treatment with 100 mg/kg TO increased glucose and decreased GCK activity while 200 mg/kg for the same duration increased glucose, insulin, GCK and G6Pase activities but reduced glucagon. The 14-day treatment with 100 mg/kg TO decreased glucose and glucagon but increased cortisol, while 200 mg/kg TO for same duration increased insulin, but reduced glucagon and GCK activity.
Conclusion: The TO's post-hypoglycaemic hyperglycaemia results from increased glucagon and G6Pase activity, and reduced GCK activity. Moreover, the glucagon response mainly depends on glucose rather than insulin.
Keywords: ANOVA, Analysis of Variance; Avidin-HRP, Avidin-Horseradish Peroxidase; Counter-regulatory hormones; EGP, Endogenous glucose production; ELISA, Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; G6P, Glucose-6-phosphate; G6PD, Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; G6Pase, Glucose-6-phosphatase; GCK, Glucokinase; Glucoregulatory enzymes; Insulin; LDH, Lactate dehydrogenase; LSD, Least Significance Difference; NAD, Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NIH, National Institutes of Health; Plasma glucose; SEM, Standard error of mean; SPSS, Statistical Package for the Social Sciences; TO, Telfairia occidentalis; Telfairia occidentalis; cAMP, Cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Telfairia occidentalis stimulates hepatic glycolysis and pyruvate production via insulin-dependent and insulin-independent mechanisms.Metabol Open. 2021 Apr 14;10:100092. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2021.100092. eCollection 2021 Jun. Metabol Open. 2021. PMID: 33997754 Free PMC article.
-
Incretin hormones and maturity onset diabetes of the young--pathophysiological implications and anti-diabetic treatment potential.Dan Med J. 2015 Sep;62(9):B4860. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 26324089 Clinical Trial.
-
Post-Translational Regulation of the Glucose-6-Phosphatase Complex by Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate Is a Crucial Determinant of Endogenous Glucose Production and Is Controlled by the Glucose-6-Phosphate Transporter.J Proteome Res. 2016 Apr 1;15(4):1342-9. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00110. Epub 2016 Mar 16. J Proteome Res. 2016. PMID: 26958868
-
A report of 2 new cases of MODY2 and review of the literature: implications in the search for type 2 diabetes drugs.Metabolism. 2013 Nov;62(11):1535-42. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 23890519 Review.
-
Drug-induced disorders of glucose metabolism. Mechanisms and management.Drug Saf. 1996 Aug;15(2):135-57. doi: 10.2165/00002018-199615020-00005. Drug Saf. 1996. PMID: 8884164 Review.
Cited by
-
Telfairia occidentalis stimulates hepatic glycolysis and pyruvate production via insulin-dependent and insulin-independent mechanisms.Metabol Open. 2021 Apr 14;10:100092. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2021.100092. eCollection 2021 Jun. Metabol Open. 2021. PMID: 33997754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Okoli B.E., Mgbeogu C.M. Fluted pumpkin, Telfairia occidentalis: West African vegetable crop. Econ Bot. 1983;37:145–149. doi: 10.2307/4254473. - DOI
-
- Akoroda M.O. Seed production and breeding potential of the fluted pumpkin, Telfairia occidentalis. Euphytica. 1990;49(1):25–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00024127. - DOI
-
- Gbile Z.O. Ethnobotany, taxonomy and conservation of medicinal plants. In: Sofowora A.O., editor. The state of medicinal plants research in Nigeria. University of Ibadan Press; 1986. p. 19.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

