Viruses join the circular RNA world
- PMID: 33236482
- PMCID: PMC7753765
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.15639
Viruses join the circular RNA world
Abstract
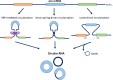
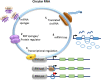
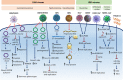
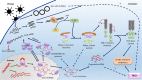
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a recently discovered class of noncoding RNAs found in many species across the eukaryotic kingdom. These intriguing RNA species are formed through a unique mechanism that is known as back splicing in which the 5' and 3' termini are covalently joined. Recent research has revealed that viruses also encode a repertoire of circRNAs. Some of these viral circRNAs are abundantly expressed and are reported to play a role in disease pathogenesis. A growing number of studies also indicate that host circRNAs are involved in immune responses against virus infections with either an antiviral or proviral role. In this review, we briefly introduce circRNA, its biogenesis, and mechanism of action. We go on to summarize the latest research on the expression, regulation, and functions of viral and host-encoded circRNAs during the host-virus interaction, with the aim of highlighting the potential of viral and host circRNAs as a suitable target for diagnostic biomarker development and therapeutic treatment of viral-associated diseases. We conclude by discussing the current limitations in knowledge and significance of elucidating the roles of circRNAs in host-virus interactions, as well as future directions for this emerging field.
Keywords: circRNA; circular RNA; miRNA sponge; noncoding RNA; virus.
© 2020 Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bieniasz PD (2004) Intrinsic immunity: a front‐line defense against viral attack. Nat Immunol 5, 1109–1115. - PubMed
-
- Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer M et al, (2013) Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 495, 333–338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

