Recent Progress in the Synergistic Combination of Nanoparticle-Mediated Hyperthermia and Immunotherapy for Treatment of Cancer
- PMID: 33236511
- PMCID: PMC8034553
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202001415
Recent Progress in the Synergistic Combination of Nanoparticle-Mediated Hyperthermia and Immunotherapy for Treatment of Cancer
Abstract
Immunotherapy has demonstrated great clinical success in certain cancers, driven primarily by immune checkpoint blockade and adoptive cell therapies. Immunotherapy can elicit strong, durable responses in some patients, but others do not respond, and to date immunotherapy has demonstrated success in only a limited number of cancers. To address this limitation, combinatorial approaches with chemo- and radiotherapy have been applied in the clinic. Extensive preclinical evidence suggests that hyperthermia therapy (HT) has considerable potential to augment immunotherapy with minimal toxicity. This progress report will provide a brief overview of immunotherapy and HT approaches and highlight recent progress in the application of nanoparticle (NP)-based HT in combination with immunotherapy. NPs allow for tumor-specific targeting of deep tissue tumors while potentially providing more even heating. NP-based HT increases tumor immunogenicity and tumor permeability, which improves immune cell infiltration and creates an environment more responsive to immunotherapy, particularly in solid tumors.
Keywords: cancer; immunotherapy; magnetic hyperthermia therapy; nanoparticles; photothermal therapy.
© 2020 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


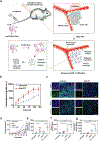
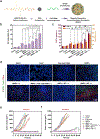
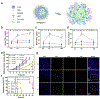
References
-
- Vinay DS, Ryan EP, Pawelec G, Talib WH, Stagg J, Elkord E, Lichtor T, Decker WK, Whelan RL, Kumara HMCS, Signori E, Honoki K, Georgakilas AG, Amin A, Helferich WG, Boosani CS, Guha G, Ciriolo MR, Chen S, Mohammed SI, Azmi AS, Keith WN, Bilsland A, Bhakta D, Halicka D, Fujii H, Aquilano K, Ashraf SS, Nowsheen S, Yang X, Choi BK, Kwon BS, Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, DOI 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.03.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

