In silico modelling and characterization of eight blast resistance proteins in resistant and susceptible rice cultivars
- PMID: 33237489
- PMCID: PMC7688789
- DOI: 10.1186/s43141-020-00076-0
In silico modelling and characterization of eight blast resistance proteins in resistant and susceptible rice cultivars
Abstract
Background: Nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat (NBS-LRR) resistance genes are the largest class of plant resistance genes which play an important role in the plant defense response. These genes are better conserved than others and function as a recognition-based immune system in plants through their encoded proteins.
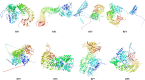
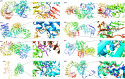
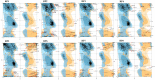
Results: Here, we report the effect of Magnaporthe oryzae, the rice blast pathogen inoculation in resistant BR2655 and susceptible HR12 rice cultivars. Transcriptomic profiling was carried out to analyze differential gene expression in these two cultivars. A total of eight NBS-LRR uncharacterized resistance proteins (RP1, RP2, RP3, RP4, RP5, RP6, RP7, and RP8) were selected in these two cultivars for in silico modeling. Modeller 9.22 and SWISS-MODEL servers were used for the homology modeling of eight RPs. ProFunc server was utilized for the prediction of secondary structure and function. The CDvist Web server and Interpro scan server detected the motif and domains in eight RPs. Ramachandran plot of eight RPs confirmed that the modeled structures occupied favorable positions.
Conclusions: From the present study, computational analysis of these eight RPs may afford insights into their role, function, and valuable resource for studying the intricate details of the plant defense mechanism. Furthermore, the identification of resistance proteins is useful for the development of molecular markers linked to resistance genes.
Keywords: Homology modeling; In silico analysis; NBS-LRR; Resistance proteins; Rice blast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Sharma K, Antunes IL, Rajulapati V, Goyal A. Low-resolution SAXS and comparative modelling based structure analysis of endo-β-1, 4-xylanase a family 10 glycoside hydrolase from Pseudopedobacter saltans comb. nov. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;112:1104–1114. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.037. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gururani MA, Venkatesh J, Upadhyaya CP, et al. Plant disease resistance genes: current status and future directions. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol. 2012;78:51–65. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2012.01.002. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
