Primary Sulfonamide Synthesis Using the Sulfinylamine Reagent N-Sulfinyl- O-(tert-butyl)hydroxylamine, t-BuONSO
- PMID: 33237777
- PMCID: PMC7754190
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c03505
Primary Sulfonamide Synthesis Using the Sulfinylamine Reagent N-Sulfinyl- O-(tert-butyl)hydroxylamine, t-BuONSO
Abstract
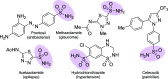
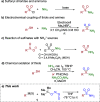
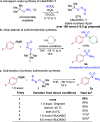
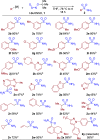
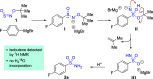
Sulfonamides have played a defining role in the history of drug development and continue to be prevalent today. In particular, primary sulfonamides are common in marketed drugs. Here we describe the direct synthesis of these valuable compounds from organometallic reagents and a novel sulfinylamine reagent, t-BuONSO. A variety of (hetero)aryl and alkyl Grignard and organolithium reagents perform well in the reaction, providing primary sulfonamides in good to excellent yields in a convenient one-step process.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Petkowski J. J.; Bains W.; Seager S. Natural Products Containing a Nitrogen-Sulfur Bond. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 423–446. 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00921. - DOI - PubMed
- Mujumdar P.; Poulsen S. A. Natural Product Primary Sulfonamides and Primary Sulfamates. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1470–1477. 10.1021/np501015m. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wright J. M.; Musini V. M.. First-line drugs for hypertension. Cochrane Db Syst. Rev. 2009. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

