Transiently "Undead" Enterocytes Mediate Homeostatic Tissue Turnover in the Adult Drosophila Midgut
- PMID: 33238125
- PMCID: PMC7754855
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108408
Transiently "Undead" Enterocytes Mediate Homeostatic Tissue Turnover in the Adult Drosophila Midgut
Abstract
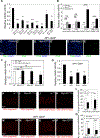
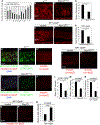
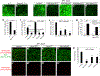
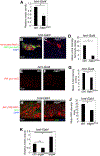
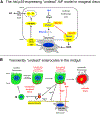
We reveal surprising similarities between homeostatic cell turnover in adult Drosophila midguts and "undead" apoptosis-induced compensatory proliferation (AiP) in imaginal discs. During undead AiP, immortalized cells signal for AiP, allowing its analysis. Critical for undead AiP is the Myo1D-dependent localization of the initiator caspase Dronc to the plasma membrane. Here, we show that Myo1D functions in mature enterocytes (ECs) to control mitotic activity of intestinal stem cells (ISCs). In Myo1D mutant midguts, many signaling events involved in AiP (ROS generation, hemocyte recruitment, and JNK signaling) are affected. Importantly, similar to AiP, Myo1D is required for membrane localization of Dronc in ECs. We propose that ECs destined to die transiently enter an undead-like state through Myo1D-dependent membrane localization of Dronc, which enables them to generate signals for ISC activity and their replacement. The concept of transiently "undead" cells may be relevant for other stem cell models in flies and mammals.
Keywords: Dronc; Drosophila melanogaster; Duox; JNK; Myo1D; apoptosis-induced proliferation; enterocyte; hemocyte; posterior midgut; undead state.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bach EA, Ekas LA, Ayala-Camargo A, Flaherty MS, Lee H, Perrimon N, and Baeg GH (2007). GFP reporters detect the activation of the Drosophila JAK/STAT pathway in vivo. Gene Expr. Patterns 7, 323–331. - PubMed
-
- Barylko B, Binns DD, and Albanesi JP (2000). Regulation of the enzymatic and motor activities of myosin I. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1496, 23–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

