An Overview of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Inflammation
- PMID: 33238435
- PMCID: PMC7700122
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25225474
An Overview of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Inflammation
Abstract
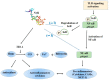
Inflammation is a key driver in many pathological conditions such as allergy, cancer, Alzheimer's disease, and many others, and the current state of available drugs prompted researchers to explore new therapeutic targets. In this context, accumulating evidence indicates that the transcription factor Nrf2 plays a pivotal role controlling the expression of antioxidant genes that ultimately exert anti-inflammatory functions. Nrf2 and its principal negative regulator, the E3 ligase adaptor Kelch-like ECH- associated protein 1 (Keap1), play a central role in the maintenance of intracellular redox homeostasis and regulation of inflammation. Interestingly, Nrf2 is proved to contribute to the regulation of the heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) axis, which is a potent anti-inflammatory target. Recent studies showed a connection between the Nrf2/antioxidant response element (ARE) system and the expression of inflammatory mediators, NF-κB pathway and macrophage metabolism. This suggests a new strategy for designing chemical agents as modulators of Nrf2 dependent pathways to target the immune response. Therefore, the present review will examine the relationship between Nrf2 signaling and the inflammation as well as possible approaches for the therapeutic modulation of this pathway.
Keywords: Keap1; Nrf2; inflammation; oxidative stress; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Soehnlein O., Lindbon L. Phagocyte partnership during the onset and resolution of inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010;10:427–439. - PubMed
-
- Janeway C.A., Travers P., Walport M., Shlomchik M.J. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease. Garland Science; New York, NY, USA: 2005.
-
- Noah T.A., Zachary M.W., Randy J.N. Inflammation: Mechanisms, costs, and natural variation. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012;43:385–406.
-
- Kaulmann A., Bohn T. Carotenoids, inflammation, and oxidative stress–implications of cellular signaling pathways and relation to chronic disease prevention. Nutr. Res. 2014;34:907–929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

