Hidden Host Mortality from an Introduced Parasitoid: Conventional and Molecular Evaluation of Non-Target Risk
- PMID: 33238441
- PMCID: PMC7700454
- DOI: 10.3390/insects11110822
Hidden Host Mortality from an Introduced Parasitoid: Conventional and Molecular Evaluation of Non-Target Risk
Abstract
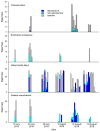
Hidden trophic interactions are important in understanding food web ecology and evaluating the ecological risks and benefits associated with the introduction of exotic natural enemies in classical biological control programs. Although non-target risk is typically evaluated based on evidence of successful parasitism, parasitoid-induced host mortality not resulting in visible evidence of parasitism (i.e., nonreproductive effects) is often overlooked. The adventive establishment of Trissolcus japonicus, an exotic parasitoid of the introduced stink bug Halyomorpha halys, provides an opportunity to investigate the total impact of this parasitoid on target and non-target hosts in the field. We developed a new methodology to measure nonreproductive effects in this system, involving a species-specific diagnostic PCR assay for T. japonicus. We applied this methodology to field-deployed eggs of four pentatomid species, coupled with traditional rearing techniques. Nonreproductive effects were responsible for the mortality of an additional 5.6% of H. halys eggs due to T. japonicus, and were even more substantial in some of the non-target species (5.4-43.2%). The observed hidden mortality of native non-target species from an introduced parasitoid could change predictions about direct and indirect ecological interactions and the efficacy of biological control of the target pest.
Keywords: Halyomorpha halys; Trissolcus japonicus; hidden mortality; indirect effects; molecular forensics; non-target; nonreproductive effects; parasitoid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





References
-
- Heimpel G.E., Mills N.J. Biological Control. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 2017.
-
- Howarth F.G. Environmental impacts of classical biological control. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 1991;36:485–509.
-
- Heimpel G.E., Cock M.J. Shifting paradigms in the history of classical biological control. BioControl. 2018;63:27–37.
-
- Barratt B.I.P., Blossey B., Hokkanen H.M. Post-release evaluation of non-target effects of biological control agents. In: Bigler F., Babendreier D., Kuhlmann U., editors. Environmental Impact of Invertebrates for Biological Control of Arthropods: Methods and Risk Assessment. CABI Publishing; Wallingford, UK: 2006. pp. 166–186.
-
- Van Lenteren J.C., Bale J., Bigler F., Hokkanen H.M.T., Loomans A.J.M. Assessing risks of releasing exotic biological control agents of arthropod pests. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2006;51:609–634. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- SCRI Grant #2016-51181-25409/U.S. Department of Agriculture
- Hatch project 1016563/U.S. Department of Agriculture
- A-BASE #2362/Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada
- Identification, monitoring, and redistribution of Trissolcus japonicus- Biological Control of Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (BMSB)/Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services-Division of Plant Industry and USDA
- CP-16-101/Washington Tree Fruit Research Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

