Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy and Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction
- PMID: 33238806
- PMCID: PMC9853919
- DOI: 10.1177/1073858420954811
Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy and Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction
Abstract
Cerebral hemorrhage, a devastating subtype of stroke, is often caused by hypertension and cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA). Pathological evidence of CAA is detected in approximately half of all individuals over the age of 70 and is associated with cortical microinfarcts and cognitive impairment. The underlying pathophysiology of CAA is characterized by accumulation of pathogenic amyloid β (Aβ) fragments of amyloid precursor protein in the cerebral vasculature. Vascular deposition of Aβ damages the vessel wall, results in blood-brain barrier (BBB) leakiness, vessel occlusion or rupture, and leads to hemorrhages and decreased cerebral blood flow that negatively affects vessel integrity and cognitive function. Currently, the main hypothesis surrounding the mechanism of CAA pathogenesis is that there is an impaired clearance of Aβ peptides, which includes compromised perivascular drainage as well as dysfunction of BBB transport. Also, the immune response in CAA pathogenesis plays an important role. Therefore, the mechanism by which Aβ vascular deposition occurs is crucial for our understanding of CAA pathogenesis and for the development of potential therapeutic options.
Keywords: BBB; CAA; amyloid beta; inflammation; intracerebral hemorrhage.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures




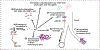

References
-
- Akiyama H, Kondoh T, Kokunai T, Nagashima T, Saito N, Tamaki N. 2000. Blood-brain barrier formation of grafted human umbilical vein endothelial cells in athymic mouse brain. Brain Res 858(1):172–6. - PubMed
-
- Attems J, Quass M, Jellinger KA, Lintner F. 2007. Topographical distribution of cerebral amyloid angiopathy and its effect on cognitive decline are influenced by Alzheimer disease pathology. J Neurol Sci 257(1–2):49–55. - PubMed
-
- Auriel E, Greenberg SM. 2012. The pathophysiology and clinical presentation of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Curr Atheroscler Rep 14(4):343–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

