The potential role of serum angiotensin-converting enzyme in coronavirus disease 2019
- PMID: 33238910
- PMCID: PMC7686943
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-020-05619-x
The potential role of serum angiotensin-converting enzyme in coronavirus disease 2019
Abstract
Background: To explore the clinical significance of serum angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) activity in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Methods: In this retrospective study, a total of 136 consecutive patients with confirmed COVID-19 were recruited. Demographic and clinical data were recorded. The serum ACE activity was measured at baseline and during the recovery phase, and its relationship with clinical condition was analyzed.
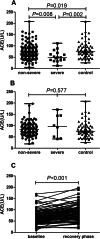
Results: Of the 136 patients with confirmed COVID-19, the 16 severe patients were older and had a higher body mass index (BMI) and proportion of hypertension than the 120 nonsevere patients. In comparison to those of normal controls, the baseline serum ACE activities of subjects in the severe group and nonsevere group were decreased, with the lowest level in the severe group. However, the serum ACE activity increased in the recovery phase, and there were no significant differences among the severe group, nonsevere group and normal control group.
Conclusion: Serum ACE activity could be used as a marker to reflect the clinical condition of COVID-19 since low activity was associated with the severity of COVID-19 at baseline, and the activity increased with the remission of the disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; Clinical significance; SARS-CoV-2; Serum ACE.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2020HMZD18/COVID-19 Platform Program of Hwa Mei Hospital, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
- 2020HMZD21/COVID-19 Platform Program of Hwa Mei Hospital, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
- 2020HMZD27/COVID-19 Platform Program of Hwa Mei Hospital, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
- LGF21H010005/Zhejiang Provincial Public Service and Application Research Foundation, China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

