Elucidation of DNA Repair Function of PfBlm and Potentiation of Artemisinin Action by a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of RecQ Helicase
- PMID: 33239368
- PMCID: PMC7690958
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.00956-20
Elucidation of DNA Repair Function of PfBlm and Potentiation of Artemisinin Action by a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of RecQ Helicase
Abstract
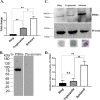
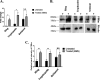
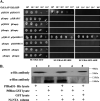
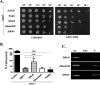
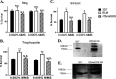
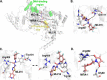
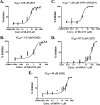
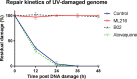
Artemisinin (ART)-based combination therapies are recommended as first- and second-line treatments for Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Here, we investigated the impact of the RecQ inhibitor ML216 on the repair of ART-mediated damage in the genome of P. falciparumPfBLM and PfWRN were identified as members of the RecQ helicase family in P. falciparum However, the role of these RecQ helicases in DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair in this parasite has not been explored. Here, we provide several lines of evidence to establish the involvement of PfBlm in DSB repair in P. falciparum First, we demonstrate that PfBlm interacts with two well-characterized DSB repair proteins of this parasite, namely, PfRad51 and PfalMre11. Second, we found that PfBLM expression was upregulated in response to DNA-damaging agents. Third, through yeast complementation studies, we demonstrated that PfBLM could complement the DNA damage sensitivity of a Δsgs1 mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, in contrast to the helicase-dead mutant PfblmK83R Finally, we observe that the overexpression of PfBLM induces resistance to DNA-damaging agents and offers a survival advantage to the parasites. Most importantly, we found that the RecQ inhibitor ML216 inhibits the repair of DSBs and thereby renders parasites more sensitive to ART. Such synergism between ART and ML216 actions was observed for both drug-sensitive and multidrug-resistant strains of P. falciparum Taken together, these findings establish the implications of PfBlm in the Plasmodium DSB repair pathway and provide insights into the antiparasitic activity of the ART-ML216 combination.IMPORTANCE Malaria continues to be a serious threat to humankind not only because of the morbidity and mortality associated with the disease but also due to the huge economic burden that it imparts. Resistance to all available drugs and the unavailability of an effective vaccine cry for an urgent discovery of newer drug targets. Here, we uncovered a role of the PfBlm helicase in Plasmodium DNA double-strand break repair and established that the parasitic DNA repair mechanism can be targeted to curb malaria. The small-molecule inhibitor of PfBlm tested in this study acts synergistically with two first-line malaria drugs, artemisinin (ART) and chloroquine, in both drug-sensitive and multidrug-resistant strains of P. falciparum, thus qualifying this chemical as a potential partner in ART-based combination therapy. Additionally, the identification of this new specific inhibitor of the Plasmodium homologous recombination (HR) mechanism will now allow us to investigate the role of HR in Plasmodium biology.
Keywords: DNA repair; PfBlm; PfWrn; Plasmodium falciparum; homologous recombination; molecular docking; yeast complementation.
Copyright © 2020 Suthram et al.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
